Have you ever wondered about the definition of a distant cousin? We often hear about our immediate family members, such as parents, siblings, and grandparents, but distant relatives are also an important part of our family tree. In this blog post, we will explore the meaning of distant cousin and shed some light on this lesser-known aspect of our family relationships.
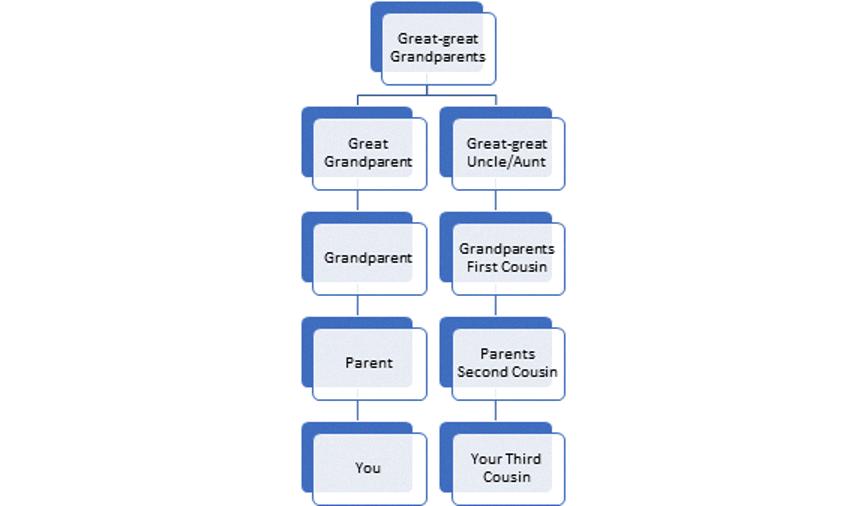
Firstly, let’s understand what a distant cousin means. A distant cousin is a relative who is not closely related to you. This means that they are beyond the immediate family circle, which includes parents, siblings, children, aunts, uncles, nieces, nephews, grandparents, and grandchildren. Examples of distant relatives include great-aunts, cousins, and second cousins.
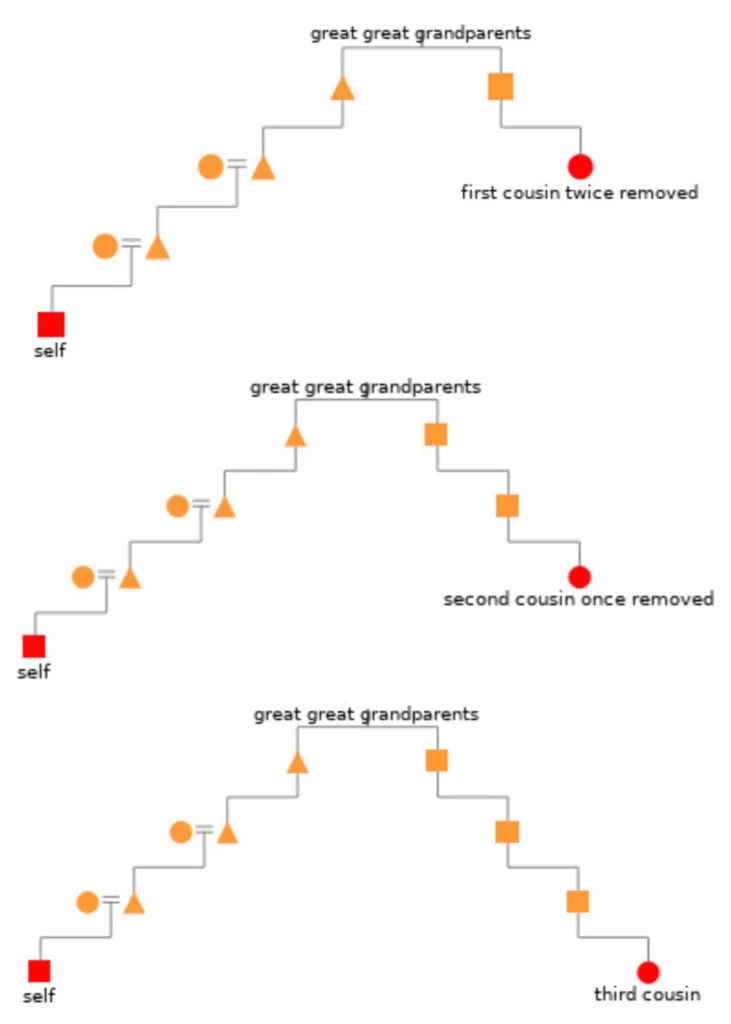
Now, let’s take a closer look at the different levels of cousin relationships. First cousins share a grandparent, which means they are two generations apart. Second cousins share a great-grandparent, which means they are three generations apart. Third cousins share a great-great-grandparent, which means they are four generations apart. Finally, fourth cousins share a 3rd-great grandparent, which means they are five generations apart. Any cousin relationship beyond fourth cousins is considered distant cousins.
It’s important to note that distant cousins are still considered family as long as they are direct blood descendants from a shared common ancestor. This means that if you have a distant cousin who is a fifth or sixth cousin, you are still connected through your family lineage. In fact, scientists estimate that the furthest cousin on Earth we each have is a 70th cousin which means we are all related to each other through our common ancestors.
While you may not interact with your distant cousins on a regular basis, it’s still important to acknowledge and appreiate your connections to them. Understanding your family history and lineage can be a powerful tool for building a sense of identity and belonging. Additionally, reaching out to distant cousins can be a great way to expand your support network and learn more about your family’s past.
In conclusion, distant cousins may not be the first family members that come to mind when we think about our relatives, but they are an important part of our family tree. By understanding the meaning of distant cousin relationships, we can appreciate the depth and complexity of our family connections. So the next time you come across a distant cousin, remember that you share a piece of your family history and lineage.
Understanding the Meaning of Being a Distant Relative
Being a distant relative means being related to someone, but not in a direct or close manner. This means that distant relatives are not immediate family members such as parents, siblings, children, aunts, uncles, nieces, nephews, grandparents, and grandchildren. Instead, distant relatives are those who are further removed from your immediate family tree such as cousins, great-aunts, second cousins, and so on. Distant relatives may share a common ancestor with you, but the degree of separation is greater than that of immediate family members. While distant relatives may not be as closely connected as immediate family members, they can sill be important family connections and may hold significance in terms of family history, inheritance, and genealogy.
Source: namecensus.com
Determining the Distance of a Cousin
To determine if your cousin is distant, you need to consider the degree of relationship you share with them. Cousins can be classified into diferent degrees based on how closely related they are to you.
First cousins share a grandparent, which means they are closely related to you. Second cousins share a great-grandparent, which makes them more distant than first cousins. Third cousins share a great-great-grandparent, while fourth cousins share a 3rd-great grandparent.
To determine how many degrees of cousinship you share with someone, you need to trace your ancestry back to the common ancestor that you share. If you and your cousin have a common great-grandparent, then you are second cousins. If you share a common great-great-grandparent, then you are third cousins, and so on.
You can use a family tree or genealogy website to help you trace your ancestry and determine the degree of cousinship you share with someone. Once you know how distant your cousin is, you can better understand your relationship with them and how much genetic material you share.
Are Distant Cousins Related by Blood?
Yes, distant cousins are blood-related. They share a common ancestor, although it may be sveral generations back. The degree of blood relation decreases as the number of generations increases, but there is still a genetic connection between distant cousins. In fact, all humans are related to some extent, as we all share a common ancestor at some point in our evolutionary history. However, the genetic similarity between distant cousins is usually small enough that any potential health risks from intermarriage are negligible. Nonetheless, distant cousins are still considered family, and many people enjoy exploring their ancestry and connecting with distant relatives.
The Relationship Between Most Distant Cousins
Scientists estimate that the most distant cousin we each have on Earth is a 70th cousin. This is because we are all related through our common ancestors, Y chromosomal Adam and mitochondrial Eve, who lived in Africa a few hundred thousand years ago. Despite the vast geographic and cultural differences that exist among humans, we all share a common ancestry and are more closely related than we may realize. This realization can help foster a sense of interconnectedness and empathy towards others, regardless of our perceived differences.
Marrying a Distant Cousin: Is It Acceptable?
Marriage between distant cousins is generally allowed and legal in the United States. However, the laws regarding cousin marriage vary from state to state, so it is important to check the laws in your specific state before proceeding with marriage. In some states, first-cousin marriage is prohibited, while in others, it is allowed, but with certain restrictions.
It is also important to consider the potential genetic risks associated with cousin marriage. Children born to first cousins have a slightly higher risk of certain genetic disorders, but the risk is still relatively low. The risk decreases even furter with more distant cousins. It is recommended that individuals who are considering marrying a distant cousin consult with a genetic counselor to discuss any potential risks.
Additionally, cultural and social attitudes towards cousin marriage can vary widely, so it is important to consider the potential reaction of family and friends. Some cultures and religions have strong taboos against cousin marriage, while others view it as acceptable or even desirable.
Overall, while cousin marriage is legal and can be a personal choice, it is important to consider the potential legal, genetic, and social implications before proceeding.
The Impact of Distance on Family Relationships
Family members can become distant for various reasons. Some of the most common causes of estrangement include abuse, neglect, betrayal, bullying, unaddressed mental illness, destructive behavior, and substance abuse. In some cases, parents may not be accepting of a child’s sexual orientation, choice of spouse, gender identity, religion, or political views, which can also lead to estrangement.
Abuse and neglect can take many forms, including physical, emotional, and sexual abuse, as well as neglect of basic needs. Betrayal, such as infidelity or breaking a promise, can also cause family members to become distant. Bullying, especially if it is ongoing and severe, can also create a rift between family members.
Mental illness can also be a contributing factor to estrangement, especially when it goes untreated. Destructive behavior, such as addiction or compulsive gambling, can also create distance between family members. Substance abuse can be particularly damaging, as it can lead to erratic behavior and strained relationships.
In some cases, family members may not be accepting of one another’s differences, such as a child’s sexual orientation or religious beliefs. This lack of acceptance can create tension and ultimately lead to estrangement. It’s important to note that these differences do not necessarily have to be negative or controversial; even disagreements about lifestyle choices or career paths can cause family members to become distant.
Overall, family members can become distant for many reasons, and the causes are often complex and multifaceted. Building and maintaining healthy relationships withn a family requires communication, understanding, and acceptance.
The Relationship Between First Cousins and Distant Relatives
No, first cousins are not considered distant relatives. In fact, they are relatively close relatives. First cousins share a set of grandparents in common, which means they are only one generation removed from each other. This makes them much closer relatives than, say, second or third cousins, who share great-grandparents or great-great-grandparents, respectively. While there may be some cultural or societal variation in how people perceive the closeness of first cousins, from a biological standpoint, they are not considered distant relatives at all.
Can Cousins Have Romantic Feelings for Each Other?
Yes, it is possible for cousins to have romantic feelings for each other. However, it is important to note that such a relationship can be complicated due to the genetic risks involved in the offspring of closely related couples. In most cultures, first-cousin marriages are considered taboo and are even illegal in some countries. Social and family pressures can also make such relationships challenging to pursue. It is essential for individuals to consider the potential consequences and seek professional advice before engaging in romantic relationships with their cousins.
The Relationship Between Cousins: Are They Close Friends?
Yes, cousins can be close friends. Cousins share a special bond because they are family members who have grown up together or have a shared history. They often share similar experiences, memories, and family traditions, which can create a unique connection between them. Many cousins are also close in age, which can make it easier for them to relate to each other and enjoy similar activities.
Furthermore, cousins can offer a level of comfort and support that friends may not be able to provide. They understand the dynamics of their family and can be a source of advice or guidance dring difficult times. Cousins can also be a great source of companionship and fun, whether it’s playing games or going on adventures together.
In conclusion, while not all cousins may be close friends, it is certainly possible for cousins to form a strong and lasting friendship. The familial bond and shared experiences can create a unique and meaningful relationship that can last a lifetime.

How Much DNA Do Distant Cousins Share?
Distant cousins share varying amounts of DNA depending on their specific degree of relationship. According to the average % DNA shared by relationship, a first cousin typically shares 12.5% of their DNA with their cousin, while a first cousin once removed shares 6.25%. A second cousin shares an average of 3.13% of their DNA, and a second cousin once removed shares 1.5%. The amount of shared DNA decreases as the degree of relationship bcomes more distant. For example, a third cousin typically shares around 0.78% of their DNA, while a fourth cousin shares only around 0.2%. It’s important to note, however, that these are average values and there can be variations within each degree of relationship.
Do Distant Cousins Have Shared DNA?
Yes, distant cousins can share DNA, but the amount of DNA they share depends on how far back their common ancestor is. The further back the common ancestor, the less DNA they are likely to share. For example, first cousins share around 12.5% of their DNA, while second cousins share around 3.125%. As the degree of relationship becomes more distant, the likelihood of sharing DNA decreases. However, it is still possible for distant cousins to share small amounts of DNA due to random genetic inheritance. This is why DNA testing can sometimes uncover unexpected distant cousins. It is important to keep in mind that DNA testing can only reveal biological relationships, and does not necessarily indicae a familial or emotional connection.
What Are Non-Blood Related Cousins Called?
Non-blood related cousins are commonly referred to as cousins-in-law or distant cousins. Cousins-in-law are relatives through marriage, meaning that they are related to you because they are married to one of your blood-related cousins. Distant cousins, on the other hand, are related to you through a more distant family connection, such as a great-grandparent, great-aunt or uncle, or a cousin once or twice removed. It’s important to note that while these cousins may not have a direct blood relationship with you, they are still considered relatives and can be an important part of your family.
Marrying a Close Cousin: Is It Possible?
The closest cousin that you can legally marry varies depending on the laws of the country or state in which you reside. In the United States, second cousins are the closest relatives that can marry in all 50 states. Marriage between first cousins, on the other hand, is only legal in about half of the states. It’s important to note that while it may be legal to marry a second cousin, it’s sill important to consider potential genetic risks associated with close family intermarriage. In some cultures and religions, cousin marriage is more common and accepted than in others, so it’s important to research the laws and customs of your specific region.
The Impact of Jealousy on Cousins
Yes, cousins can get jealous of each other. The level of jealousy may vary depending on various factors such as age, gender, family dynamics, and the nature of the relationship between the cousins. Cousins who are close in age and of the same gender may be more prone to jealousy as they are more likely to be in direct competition with each other. For example, they may compete for the attention of a grandparent or for recognition within the family. However, jealousy between cousins is not aways negative and can be a natural part of growing up and learning how to navigate relationships. It is important for parents and caregivers to help children develop healthy ways of managing jealousy and resolving conflicts in a constructive manner.
Distance Between 7th Cousins
A seventh cousin is a relative who is quite distant from you in terms of familial relationships. To be more precise, a seventh cousin shares great-great-great-great-great-great grandparents with you. This means that you and your seventh cousin are both descended from different children of those 6th great-grandparents. In other words, your 5th great-grandparent was the sibling of your seventh cousin’s 5th great-grandparent. Due to the many intervening generations, a seventh cousin is someone you are likely not familiar with and may not even be aware of until you research your family tree.
Conclusion
In conclusion, distant cousins are relatives who are not closely relaed to us. They are those with whom we share a common ancestor beyond our great-great-great-grandparent’s generation. The term “distant” refers to the number of generations that separate us from our common ancestors. While distant cousins may not have the same level of closeness as immediate family members, they are still considered a part of our family. According to scientists, the furthest cousin on Earth that we each have is a 70th cousin, which highlights just how interconnected we all are through our shared ancestry. In essence, distant cousins are an important component of our family tree, and recognizing and valuing these relationships can help us to better understand our own heritage and the diversity of our global family.
