The medical term “cytosis” is an important concept in understanding the body’s cellular functions and processes. Cytosis refers to a process of cell formation, in which substances such as proteins, lipids, and other molecules are converted into cellular components. It is also used to describe the movement of cells or materials between different parts of the body.
In general, cytosis occurs when a cell takes up an external material or molecule, either through endocytosis or phagocytosis. Endocytosis is a process in which the cell membrane surrounds and engulfs an external substance, while phagocytosis is when the cell takes up particles directly from its environment. In both cases, the substance enters the cell where it can be further processed by enzymes.
Cytosis plays an important role in many bodily processes including digestion and nutrient absorption, immune response, tissue repair, and hormone production. Without proper cytotic activity, many of these processes would not be possible.
Cytotic disorders can occur when cells are unable to properly take up substances from their environment or process them correctly. Some examples include anisocytosis (unequal size of red blood cells), elliptocytosis (elliptical red cells), and phagocytosis (ingestion of cells). These disorders can lead to serious health consequences if left untreated so it’s important to seek medical attention if any symptoms arise.
To summarize, cytosis is a vital process that enables our bodies to function properly by allowing cells to take up materials from their environment and convert them into useful components. While there are some disorders related to this process that should be monitored for potential health risks, generally speaking it’s a necesary part of staying healthy and preventing disease.
Example of Cytosis
An example of cytosis is phagocytosis, which is the process by which cells take in and engulf particles such as bacteria or other foreign materials. This process is important for the body’s immune system to recognize and destroy foreign invaders. During phagocytosis, a cell extends pseudopodia (false feet) to surround the particle, forming a pocket around it. The pocket then closes up, trapping the particle inside and allowing the cell to digest it. This process can occur in both animal and plant cells.
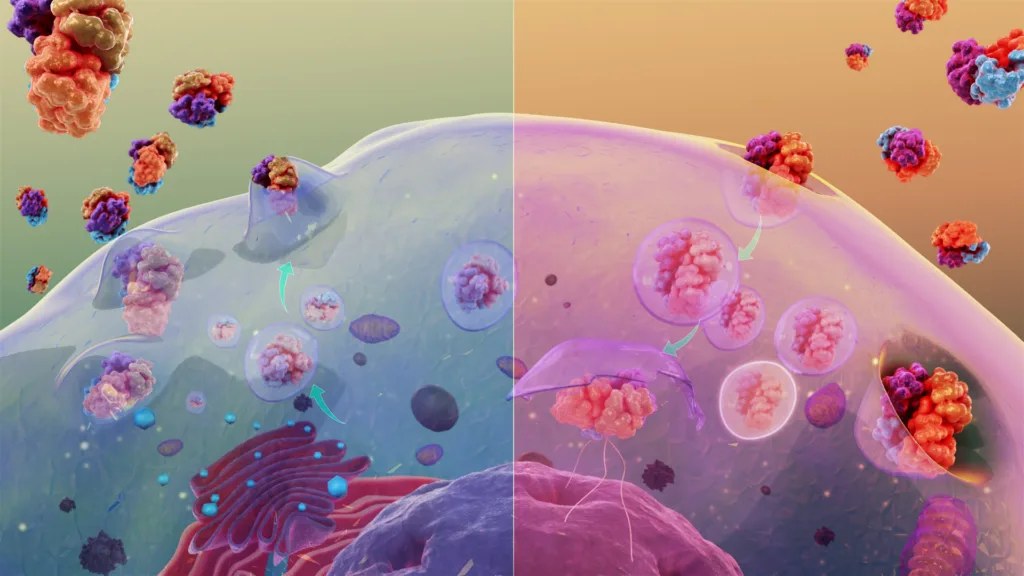
The Purpose of Cytosis
The purpose of Cytosis: A Cell Building Game is to simulate the environment of a human cell and challenge players to use their knowledge of cellular biology to build and convert cellular building blocks into enzymes, hormones, and receptors. Players must be strategic in their choices in order to maximize efficiency and score the most points. By playing Cytosis, players can gain a greater understanding of the inner workings of the human cell and become more familiar with the different components that make up the complex biological machinery.
The Meaning of Cytosis in Greek
Cytosis is derived from the Greek word kýtos, meaning “container,” “receptacle,” or “body.” It is the scientific term for an increase in the number of cells within a given area of tissue. This can occur either due to increased cell production or to reduced cell death. Cytosis can be a sign of normal physiological processes, such as growth and development, or it can be a sign of disease.
The Suffix emia Refers to Blood
The suffix that refers to blood is “-emia.” This suffix is typically used to refer to a state of the blood, either as a lack of or excess of something in the blood. For example, anemia refers to a lack of blood, while hypervolemia means an excess volume of blood. Similarly, leukocytosis refers to an elevation of white blood cells and thrombocytopenia refers to a decreased number of platelets in the bloodstream.
The Meaning of the Term ‘Cyto’
The term “cyto” is a prefix derived from the Greek word “kytos”, meaning “hollow, as a cell or container.” This prefix is used to denote a cell, and it can be found in other forms such as “-cyto-” and the suffix “-cyte”, which also refer to cells. In summary, the term “cyto” is used to describe something related to a cell or cells.
Source: meeplemountain.com
The Difference Between Cytosis and Mitosis
Yes, cytokinesis is considered part of the mitotic process. It is the final stage of mitosis, occurring after telophase, and is a physical division of the cell that separates the newly formed daughter cells. Cytokinesis typically begins with the assembly and constriction of an actin-myosin contractile ring around the middle of the cell. This contractile ring then shortens to divide the cytoplasm into two distinct parts, one for each daughter cell. At the end of cytokinesis, two new cells are formed and the mitotic process is complete.
The Effects of Cytosis on Oxygen Levels
Cytosis is a type of active transport that requires the use of ATP. The mitochondria in the cell generate ATP using oxygen, which means that oxygen levels are directly affected by the amount of cytosis taking place. When more cytosis occurs, the mitochondria require more oxygen to produce ATP, thus reducing the available oxygen in the cell. On the other hand, diffusion does not require ATP and is not affected by changes in oxygen levels.
Does Cytosis Require Energy?
Yes, cytosis does require energy. Cytosis is the process of movement of molecules or particles across the cell membrane. This process can occur through two distinct mechanisms: endocytosis and exocytosis. Both processes rely on the energy of ATP to actively transport molecules and particles across the membrane. Endocytosis involves a cell engulfing molecules or particles and moving them inside the cell; exocytosis involves a cell releasing molecules or particles out of itself. In both cases, ATP is required to power the movement of these macromolecules and large particles across the plasma membrane.
Capability of Cytosis in Blood Cells
All types of white blood cells are capable of phagocytosis, which is a process of engulfing and destroying disease-causing pathogens. This includes neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, and eosinophils. Neutrophils are most commonly associated with phagocytosis due to their abundance in the bloodstream. Monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells are all part of the innate immune system and play an important role in phagocytosing foreign invaders. Eosinophils also play a role in phagocytosis by recognizing and engulfing parasites or fungi. They produce enzymes that help break down the cell walls of these organisms, allowing them to be destroyed more effectively.
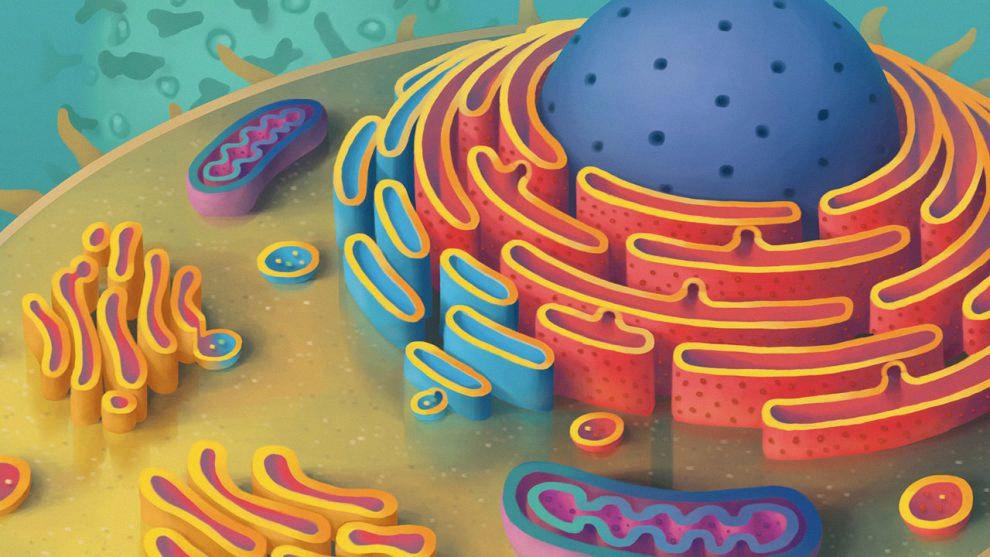
The Contents of the Cytosol
The cytosol is the aqueous solution inside a cell, and it is composed primarily of water (up to 90%) and dissolved ions such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and chloride. It also contains small molecules such as glucose and amino acids, as well as large water-soluble molecules such as proteins. In addition to these components, the cytosol may contain various metabolites, enzymes, organelles (like ribosomes), and other macromolecules. These molecules are constantly in motion within the cytosol, allowing for cellular processes such as chemical reactions and energy production.
The Meaning of ‘Cytes’ in Latin
In Latin, the suffix “-cyte” refers to a type of container or hollow vessel. It is derived from the Greek word “kutos,” which has the same meaning. This suffix is often used in scientific terms to describe a cell, organelle, or other microscopic structure that appears as a hollow, container-like structure. For example, erythrocytes are red blood cells and leukocytes are white blood cells.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cytosis is a medical term that refers to the cell building process within an organism. It involves the use of cellular building blocks such as mRNA, ATP, lipids, and glucose to create enzymes, hormones, or receptors. The root of this term cmes from the Greek kýtos meaning “container,” “receptacle,” or “body.” When combined with words or elements beginning with a vowel, it becomes cyto-. Along with cyto-, the suffix -emia is often used to refer to blood or to denote the presence of a substance in the blood. Examples of this include anemia and hypervolemia. Knowing this medical term can help one better understand how cells and other components within organisms work together for overall health and functioning.
