In physics, the coefficient of friction (or simply “friction coefficient”) is a dimensionless number used to quantify the amount of resistance two surfaces experience while sliding against each other. This number is determined by measuring the ratio between the resistive force of friction (Fr) and the normal or perpendicular force (N) pushing the objects together.
The coefficient of friction, often represented by the letter μ, is an incredibly important measure when it comes to many engineering applications, such as designing brakes or calculating how much energy can be stored in a battery. In order to ensure accuracy when dealing with these applications, it’s important to understand what units are used for measuring the friction coefficient and why.
Generally speaking, most coefficients of friction are reported in terms of newtons per meter squared (N/m2). This unit is convenient because it allows for easy calculation and comparison of different materials’ coefficients of friction. Additionally, this unit helps provide insight into how much energy must be applied in order to overcome a certain amount of frictional force—which can be very helpful in engineering applications.
Another common way to measure and report coefficients of friction is via a dimensionless number known as the “coefficient ratio”. This ratio is calculated by taking the coefficient of static friction divided by the coefficient of kinetic friction—which gives insight into how much more force must be applied in order to initiate motion between two objects compared to keeping them moving once they have started sliding against one another.
Finally, some researchers prefer to use a “coefficient index” instead—which compares relative values rather than absolute ones. A coefficient index is simply calculated by taking the product of two coefficients and dividing that result by 1 minus their difference squared. This system allows for easier comparison between materials that have different absolute coefficients on either side—making it espeially useful for comparing materials with widely varying properties.
In conclusion, understanding what units are used for measuring and reporting coefficients of friction can help engineers ensure accuracy when designing complex systems and components involving frictional forces. While newtons per meter squared is generally preferred due to its convenience, there are other options available as well—such as coefficient ratios and indexes—that may be better suited for certain applications or projects depending on their individual needs and requirements.
Understanding the Lack of Units for Coefficient of Friction
The coefficient of friction is a ratio of two forces, and thereore has no associated unit. Friction is defined as the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. When two objects are in contact, there’s a normal force (perpendicular to the surface) that acts between them, as well as a resistive force (parallel to the surface) that acts to prevent motion. The coefficient of friction is simply the ratio of these two forces. Since it’s a ratio, it has no associated unit – it’s just a number that tells us how much one force resists the other.
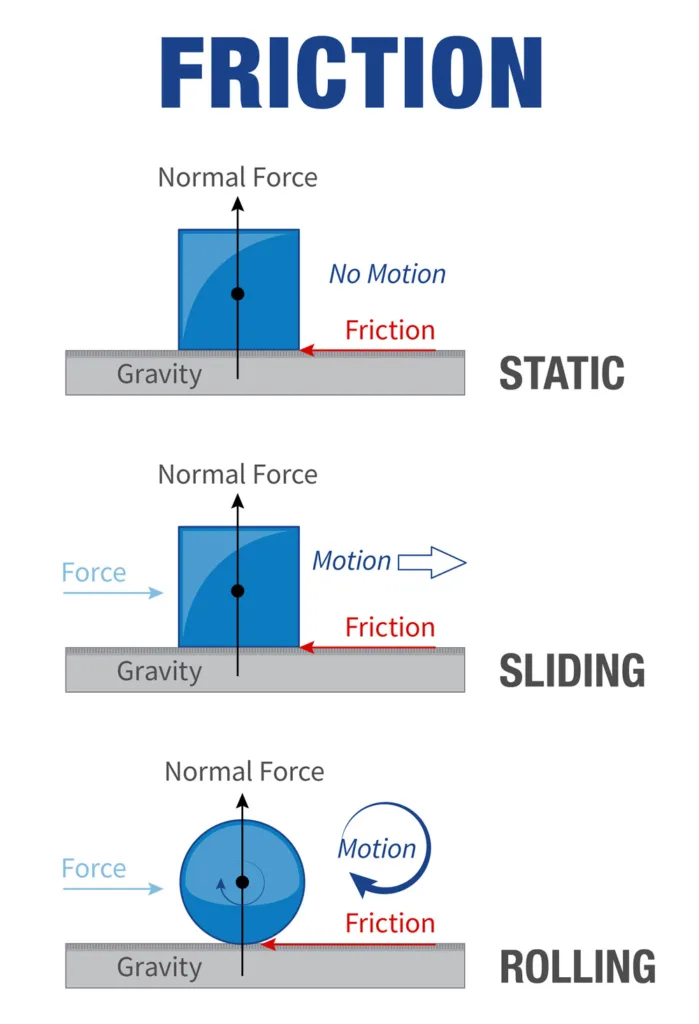
Measuring the Coefficient of Friction
The coefficient of friction can be measured in a variety of ways, depending on the type of surfaces involved. For example, if two surfaces are sliding against each other, a block and tackle or similar device can be used to measure the resistive force (Fr) when a known normal force (N) is applied. This allows for the calculation of the coefficient of friction (fr). If two objects are at rest with each other, then the coefficient of static friction can be determined by slowly increasing the normal force until motion occurs. The amount of normal force needed to initiate motion divided by the normal force will yield the coefficient of static friction. In addition to tese methods, there are also several specialized instruments that measure coefficient of friction directly.
Symbol for Coefficient of Friction
The symbol for coefficient of friction is μ (the Greek letter mu). It is a dimensionless quantity that describes the ratio of the force of friction between two surfaces and the force pressing them together. The coefficient of friction depends on the materials making up the two surfaces, as well as any lubricant between them. A higher coefficient of friction indicates more resistance to sliding, while a lower coefficient indicates less resistance.
The SI Unit of Coefficient of Friction
The SI unit of the coefficient of friction is dimensionless. This means that it does not have a unit associated with it, as it is a ratio that compares the magnitude of two forces – the force of friction and the normal force. The coefficient of friction is a measure of how much one surface resists sliding against another.
Coefficient of Friction
The coefficient of friction (μ) is a measure of the resistance to motion between two surfaces in contact with each other. It expresses the ratio of the frictional force (F) to the normal force (N) pushing the two surfaces together. In mathematical terms, this ratio is expressed as μ = F/N. This ratio can vary greatly depending on a number of factors, including the type and condition of each surface, as well as any lubricating agents or substances present. For example, a smooth metal surface in contact with anoter smooth metal surface may have a coefficient of friction value of 0.1, whereas rubber in contact with concrete may have a coefficient of friction value as high as 0.8.
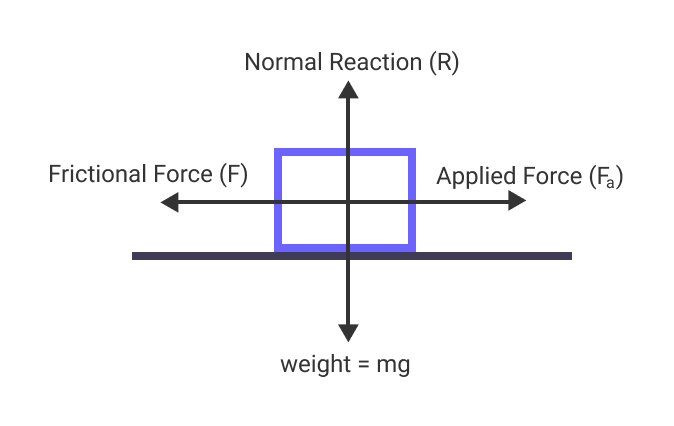
Measuring Friction in Newtons and Kilograms
Friction is measured in newtons, not kilograms. A newton is the unit of measurement for force, and it is equal to 1 kilogram-meter-per-second-squared (1 kgm/s2). This means that 1 newton of force is equal to the amount of force needed to move a mass of 1 kilogram at a rate of 1 meter per second squared. Therefore, when measuring friction, it is expressed in terms of newtons and not kilograms.
What is the Meaning of COF Value?
COF (Coefficient of Friction) is a measure of the resistance between two objects that are in contact with each other. It is calculated by dividing the force required to slide one surface over the other, by the force perpendicular to those surfaces.
The COF value indicates how easily one surface can slide over another—the lower the COF value, the less resistance there is between them and the easier it is for one surface to slip over another. COF values range from 0.00-1.00, with 0.00 indicating no resistance and 1.00 meaning complete resistance between two surfaces.
The Meaning of a Friction Coefficient of 1
A friction coefficient of 1 indicates that the frictional force between two surfaces is equal to the normal force between them. This means that it takes the same amount of force to move an object across a surface as it does to pick it up. The coefficient of friction is important in determining the amount of force required to move an object, and can be used to calculate other parameters such as speed, work, and energy. It can also help engineers decide on the right materials for certain applications.
What Does the Greek Letter ‘μ’ Represent?
μ stands for the scientific prefix micro-, which is used to indicate a value that is one millionth of a unit of measure. It is derived from the Greek letter mu, which is often used in mathematics and science to represent a reduced or scaled quantity. Micro- is commonly used in measurements such as microseconds, micrograms, and micrometers. In chemistry, it can refer to an element’s atomic mass or its molar mass, which are typically expressed in micrograms per mole (μg/mol). Additionally, in physics, it may be used to indicate very small distances or tiny particles.
Source: bbc.co.uk
The Name of μ
The name of the Greek letter μ (U+03BC) is “mu” and it is used as a unit prefix in the metric system to denote a factor of 10− 6 (one millionth). The prefix comes from the Greek word μικρός (mikrós), which means “small”. In 1960, the International System of Units officially adopted this prefix.
What Does the Greek Letter μ Mean in Mathematics?
In mathematics, the symbol ‘μ’ (or mu) is used to represent the population mean, or the average of a set of numbers. It is calculated by adding up all the values in a population and then dividing by the total number of cases present. The formula for calculating the population mean is: μ = Σ Xi / N, where Σ Xi represents the sum of all scores present in the population and N represents the total number of individuals or cases in the population.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the coefficient of friction is a dimensionless quantity, represented by the letter μ in physics. It is found by dividing the resistive force of friction (Fr) by the normal, or perpendicular force (N) pushing the objects together. As a result, the coefficient of friction does not have any associated units, making it an invaluable tool for measuring and understanding the forces between two objects.
