CHON P is an acronym used in biology to refer to the four most important elements found in living organisms: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen. These elements make up a large percentage of the mass of any living organism and are essential for life as we know it.
Carbon is the basis of all organic molecules, including proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. Carbon atoms have a unique ability to form multiple bonds with other elements and form the backbone of large complex molecules. Carbon is found in all living organisms on Earth and is essential for the creation of energy needed for life to exist.
Hydrogen is the simplest element found in nature and can be found bonded to many other elements including carbon. Hydrogen plays an important role in metabolism as it participates in redox reactions that create ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is used by cells for energy production. Hydrogen also helps form strong hydrogen bonds between molecules which helps maintain structural integrity in many biological systems.
Oxygen plays a key role in respiration, where it combines with glucose to produce energy and water as waste products. Oxygen helps regulate pH levels within cells by balancing out protons that are released during metabolic reactions. Without oxygen, cells would be unable to produce enough energy to survive and so they would quickly die off if deprived of oxygen for long periods of time.
Finally, nitrogen is present in all amino acids which are essential components of proteins that help build enzymes and other important macromolecules within cells. Nitrogen also plays an important role in DNA replication as it helps stabilize DNA strands during replication so that genetic information can be accurately passed on from one generation to the next.
Overall, CHON P are four essential elements that play an integral role in almost all biological processes within living organisms on Earth today. Without these four elements functioning together harmoniously life as we know it would not be possible!
Biomolecules (Updated)
Which Biomolecule Is CHON P?
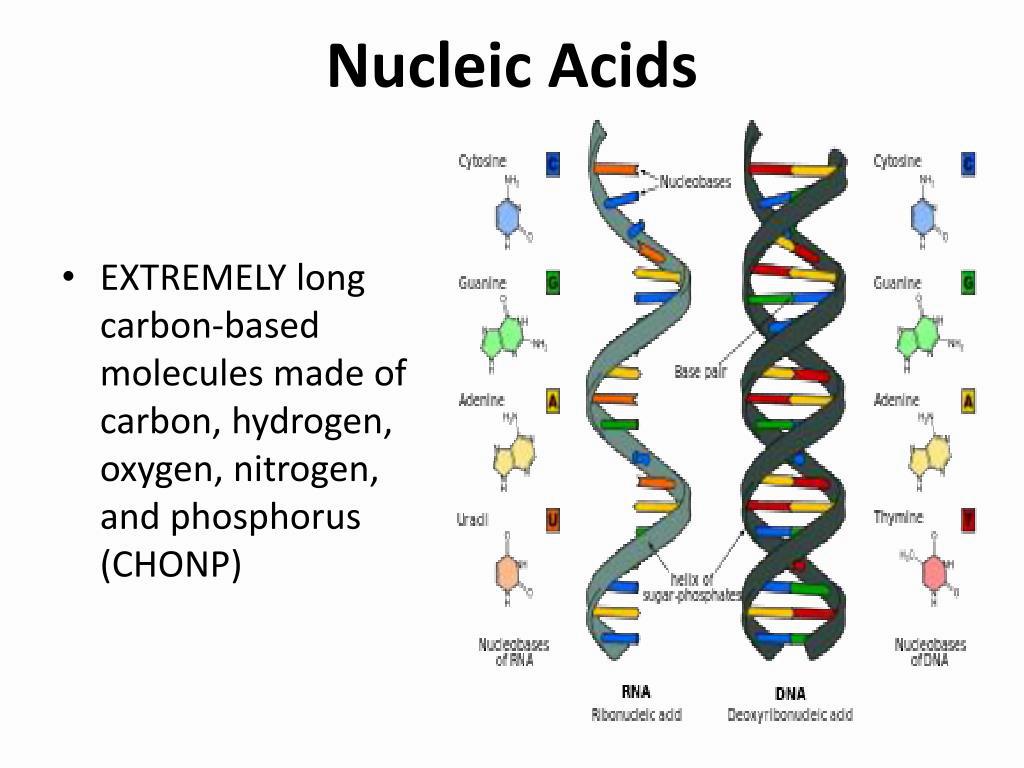
Nucleic acids are made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus (CHON P). They are key components of DNA and RNA, wich carry the genetic information of cells. Nucleotides, the building blocks of nucleic acids, are composed of a pentose sugar, a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group.
What Does Cho Cho CHON CHON P Mean?
Proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids are all made of the same elements: carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The difference between them is in the arrangement of those atoms. Proteins have a nitrogen atom in addition to the CHON elements, while carbohydrates and lipids do not. Nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA contain phosphorus in addition to the CHON elements.
What Are The 4 Biomolecules?
The four major types of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.
Carbohydrates are organic molecules that cotain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The simplest type of carbohydrate is a sugar molecule. Glucose is a sugar molecule that is used by cells to produce energy. Lipids are organic molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The simplest type of lipid is a fat molecule. Fats are used by cells to store energy. Nucleic acids are organic molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. The two types of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA. DNA is used to store genetic information. RNA is used to produce proteins. Proteins are organic molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. Proteins are used by cells to carry out their functions.
What Is Made Of CHON P?
The six chemical elements whose covalent combinations make up most biological molecules on Earth are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfur. These elements are all nonmetals, and they can be found in carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. Each of these molecules has unique properties that allow cells to interact with one another and carry out the complex processes necessary for life.
What Has CHON P Biology?
Biology is the study of life. CHON P biology refers to the six elements that make up 98% of living matter on Earth: carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfur. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in the structure and function of living organisms. For example, carbon is the main component of DNA and proteins, hydrogen is necessary for energy production, nitrogen is a key component of proteins and DNA, and oxygen is necessary for respiration. Phosphorus and sulfur are also essential for cellular function.
Is CHON P A Nucleic Acids?
Nucleic acids are molecules that play a critical role in the structure and function of all living cells. They are composed of chains of nucleotides, which are small molecules that each contain a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (either adenine [A], cytosine [C], guanine [G], or thymine [T]). The phosphate group and the sugar are linked together by a chemical bond, and the nitrogenous bases are attached to the sugar molecule in specific arrangements.
The sequence of nucleotides in a nucleic acid determines the infrmation that it carries. The genetic information in DNA is used to direct the synthesis of proteins, which carry out the essential functions of cells. RNA plays a role in protein synthesis, as well as in the transmission of genetic information from DNA to protein.
What Is The Ratio Of CHON P In Nucleic Acids?
Nucleic acids are composed of chains of nucleotides, which are each composed of a phosphate group, a sugar group, and a nitrogenous base. The ratio of CHON P in nucleic acids is 1:2:1, meaning that for every two phosphate groups there is one sugar group and one nitrogenous base.
What Is Monomeric Unit?
The monomeric unit is the smallest repeating unit of a polymer. Monomers bind to other monomers to form chains of repeating molecules through a process known as polymerization. Monomers may be eiter natural or synthetic in origin.
What Are 3 Nucleic Acids Examples?
Nucleic acids are organic molecules that store and transmit genetic information. The three most common nucleic acids are DNA, RNA, and mRNA. Each one is made up of a chain of smaller molecules called nucleotides. DNA is found in the nucleus of cells, while RNA and mRNA are found in the cytoplasm.
What Monomer Makes Up Carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates and are made up of a single sugar molecule. Glucose and fructose are the most common monosaccharides, and they are found in many differet foods. Glucose is the primary source of energy for the body, while fructose is mostly used by the liver to produce glucose.
What Is The Ratio Of C H O In Lipids?
The ratio of C:H:O in lipids is 1:2:less than one. This means that there is one carbon, two hydrogen, and less than one oxygen in each lipid molecule. Lipids are organic molecules that are found in all living cells. They are made up of the same components as water, but the ratio of these components is different. This difference allows lipids to perform different functions in the cell.
What Are The 5 Biomolecules?
1. Carbohydrates are organic molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are essential for the proper functioning of the body, and include sugars and starches.
2. Lipids are organic molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, as well as a small number of nitrogen atoms. They are essential for the proper functioning of the body, and include fats, waxes, and sterols.
3. Proteins are organic molecules that cotain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms. They are essential for the proper functioning of the body, and include enzymes, antibodies, and structural proteins.
4. Nucleic acids are organic molecules that cntain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus atoms. They are essential for the proper functioning of the body, and include DNA and RNA.
5. Water is a simple molecule that contains two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. It is essential for life and makes up aout 60% of the human body.
What Are Micromolecules Give Example?
Micromolecules are tiny molecules that are essential for life. They include sugars, amino acids, nucleic acids, fatty acids, water, and minerals. Each of these molecules is incredibly important for the body to function properly. For example, sugars are necessary for energy production, amino acids are needed to build proteins, nucleic acids play a role in cell replication, fatty acids are essential for cell membrane function, and water helps regulate body temperature and transports nutrients and waste products.
What Are Lipids Made Of?
Lipids are made of a glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid tails, and a phosphate group. The fatty acid tails are hydrophobic, whie the phosphate group is hydrophilic. As such, phospholipids are amphipathic.
