Carbon is one of the most important elements in the universe, forming the foundation for all life. But what exactly is its charge ion? To answer this question, we need to look at how carbon atoms interact with other atoms and how they form different compounds.
At a basic level, carbon has 4 electrons in its valence shell or outermost shell. This means that it can lose or gain 4 electrons in order to complete its octet – the number of electrons needed to achieve stability. To do this, it shares its valence electrons with other atoms and forms covalent bonds. This is why its charge is 4⁺. Neutral carbon-12 (or any carbon atom) has 6 electrons with a total negative charge of 6e- orbiting a nucleus with a total positive charge of 6e+, so that the total net charge is zero.
When two oxygen atoms are single bonded to carbon, then the formal charge of each atom will be 0. Carbon will have +2 charge, while each oxygen atom will have -1. This makes sense since oxygen needs two more electrons to fill up its octet and carbon can provide them through covalent bonding.
On the other hand, when carbon forms an ionic compound with another element such as silicon, it gains four electrons forming carbide (C4 -) and silicide (Si4 -) anions. This process is known as oxidation and gives the resulting compound an overall negative charge due to the excess of negatively charged ions present in it.
In conclusion, understanding carbon’s charge ion can help us understand how this essential element interacts with other elements and forms varius compounds which are essential for life on earth. With that being said, further research is necessary to get a better grasp on all aspects of this important topic!
Charge of Carbon
The charge of carbon is +4. This is because carbon has 4 electrons in its valence shell, which is its outermost shell. In order to complete its octet, it can either lose or gain 4 electrons and forms covalent bonds by sharing these electrons with other atoms. Thus, the charge of carbon is +4.
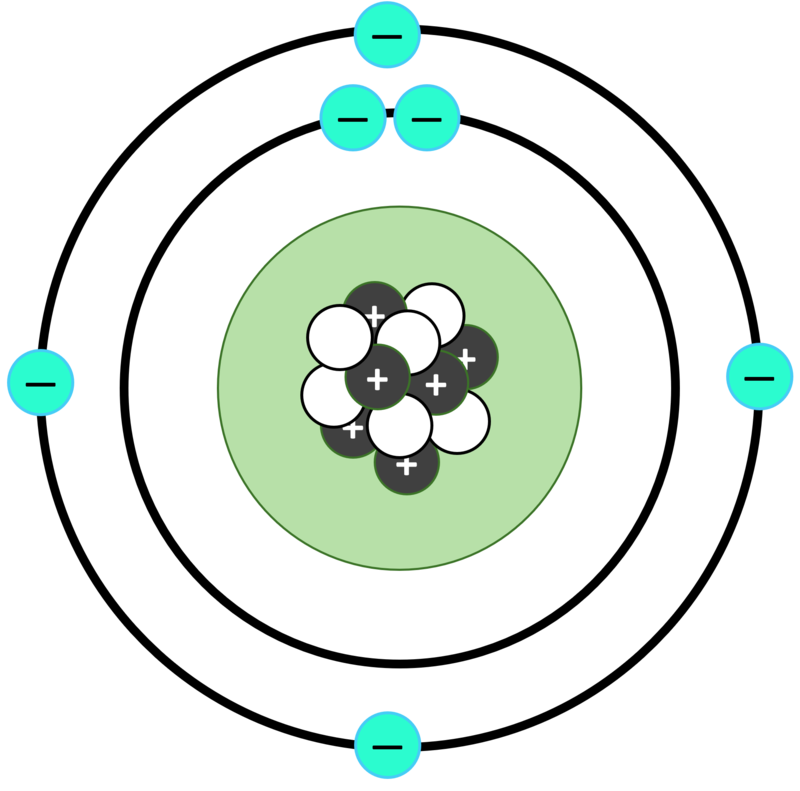
The Charge of Carbon: Positive or Negative?
Carbon is neither a negative nor a positive ion. It is a neutral atom, meaning that it has an equal number of protons and electrons in its nucleus, so the total positive charge of the protons and the total negative charge of the electrons cancel each other out, resulting in a net charge of zero.
Ionic Charge of Carbon in CO2
The ionic charge of carbon in CO2 is +2. This is because each oxygen atom has a charge of -1, while the carbon atom has a total of 2 bonds to the oxygen atoms, meaning it has a charge of +2. This is known as double-bonded carbon, and it is the reason why CO2 has a neutral formal charge overall.
Does Carbon Have an Ion?
Yes, carbon can form ions. It is capable of forming both cations and anions. When it gains four electrons, it forms the carbide anion (C4-). Alternatively, when it loses four electrons, it forms the carbon cation (C4+). Carbon also forms other monatomic ions, including C2+ and C6+, as well as polyatomic ions such as CO32-.
What Type of Ion is C4?
C 4 is a carbide ion, which is an anion with a charge of 4−. It is composed of one carbon atom with four electrons, forming a covalent bond with the four negatively charged electrons. Carbide ions are important in many chemical processes, including reactions that involve the transfer of electrons between atoms or molecules. They can also form complexes with metals, such as cobalt and nickel, to form hard alloys used in industry.
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Ionization of Carbon
Carbon is a nonmetallic element that has four valence electrons and belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. It forms covalent bonds between other atoms by sharing its electrons with them, making it a tetravalent ion. Carbon can also exist in other ionic forms in some compounds, such as dicarbon monoxide (CO2), where the carbon atom has an oxidation state of -2 and carries two negative charges.
The Positive Ionization of Carbon
Carbon is a positive ion because it does not fulfill the octet rule. When carbon has three bonds and an unfilled valence shell, it will have a formal charge of +1. This happens because the number of electrons in its outer shell is fewer than what is needed to achieve a full octet, so it must make up for this deficit by having a positive charge. In other words, when carbon has three bonds, it needs to borrow an electron from another atom in order to achieve the octet rule and becoe stable. This creates a positive charge on the carbon atom.
The Negative Ionization of Carbon
Carbon is a negative ion because it has an extra electron, giving it a negative charge. This extra electron was most likely added to the atom through chemical bonding with another atom. Carbon atoms have a tendency to form cations due to their relatively low ionization energy, which is the energy required to remove an electron from the atom. When this energy is low, it is relatively easy for other atoms or molecules to donate electrons and create negative ions.
Is Carbon an Ion or Anion?
Carbon is an atom that can form both cations and anions depending on its environment. When bonded to other elements, carbon can form cations by losing electrons and forming a positive charge, or it can form anions by gaining electrons and forming a negative charge. Carbon is also able to form molecules with itself, such as in the case of carbon dioxide (CO2), which has two oxygen atoms bonded to one carbon atom through covalent bonds. In this case, the carbon atom does not have a charge as it has gained and lost the same number of electrons.

Does Carbon Have a Charge of One?
No, carbon does not have a charge of 1. Carbon is an element in Group 14 of the periodic table and it typically has an atomic number of 6, meaning that it has 6 protons and 6 electrons. In its neutral state, these electrons are evenly distributed among its four valence shells, giving each atom a formal charge of zero. Carbon can form ionic bonds with other elements or molecules by donating or accepting electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge on the carbon atom, but this charge is typically not +1.
Does Carbon Have a Negative Charge?
Yes, carbon has a negative charge. This is because it has four electrons in its outer shell, which is full. To balance out this negative charge, oxygen, which has six electrons in its outer shell, has a positive charge. These two charges cancel each other out, resulting in an overall neutral molecule.
Charge of Carbon Atom
The charge of a carbon atom is +6, which can be determined by its atomic number. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that it has 6 protons in the nucleus. This positive charge on the nucleus is known as the nuclear charge, and for a carbon atom, this charge is +6.
The Charge of Carbon Monoxide
The charge for carbon monoxide (CO) is 0. This can be determined by looking at the Lewis structure for CO, which has both carbon and oxygen atoms. The formal charge of oxygen in the molecule is +1, so the overall charge of the molecule is 0 since carbon has a formal charge of 0.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the charge of carbon ion depends on the type of bond that it forms. If it forms an ionic bond with another atom, then it will take on a charge of 4⁺. However, in covalently bonded molecules, carbon can have either a +2 or 0 charge depending on the number of bonds formed and the number of electrons shared with other atoms. While carbon can form ionic compounds by gaining four electrons to form carbide and silicide anions, it is more commonly found in covalently bonded molecules.
