If your car is misfiring at idle, it can be a frustrating and potentially dangerous experience. A misfire at idle, wich is usually caused by an incorrect air/fuel mixture, can cause the vehicle to lose power or hesitate when you try to accelerate. While there are several potential causes for a misfire at idle, some of the most common are worn, improperly installed or mishandled spark plugs, faulty ignition coils, carbon tracking, and vacuum leaks.
To diagnose the cause of a misfire at idle, it’s important to start with a visual inspection of the spark plugs and wires. If they look corroded or worn out, then they will likely need to be replaced. Additionally, you should check for any vacuum leaks that could be affecting the engine’s performance. Vacuum leaks can affect air/fuel ratios and cause engine misfires.
Faulty ignition coils are another potential cause of misfires at idle and should be checked if other components appear to be functioning properly. Ignition coils convert battery voltage into high-voltage electricity that is used to ignite the fuel/air mixture in the cylinder. If an ignition coil is defective or not functioning correctly, it may not produce enough voltage to ignite the fuel/air mix in the cylinder resulting in a misfire at idle.
If all other components appear to be working correctly but your car is still experiencing a misfire at idle, then it may be time to replace your oxygen (O2) sensor. The O2 sensor monitors oxygen levels in your exhaust system and helps regulate air/fuel ratios in order to maximize engine performance and reduce emissions. If this sensor becomes faulty or isn’t functioning properly then it can cause an incorrect air/fuel ratio resulting in engine misfires at idle speed.
No matter what’s causing your car’s misfire at idle speed, it’s important to have it checked out by a qualified mechanic as soon as possible so that any potential problems can be addressed promptly before they cause more serious damage down the line. A properly running engine will help ensure your safety while driving as well as maintain optimal performance from your vehicle!
Causes of Misfire at Idle
A misfire only at idle can be caused by several factors, such as an incorrect air/fuel mixture. This can be due to a faulty O2 (oxygen) sensor, a single injector that needs cleaning, or even a vacuum leak. If the air/fuel mixture is off, it can cause the engine to misfire due to too much or too litle fuel being delivered at idle. Additionally, spark plugs may need to be cleaned or replaced if they are fouled with oil or carbon deposits. Lastly, a worn timing belt or camshaft could also cause an engine to misfire at idle.
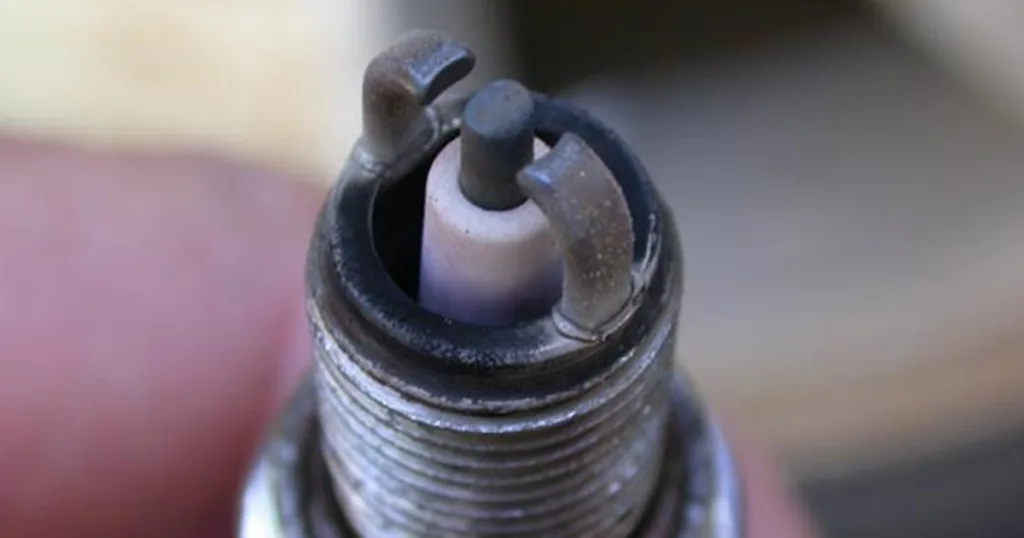

Possible Causes of a Misfire
1. Worn or improperly installed spark plugs: Spark plugs are essential components of an engine’s ignition system, and they must be functioning properly in order for the engine to run efficiently. If the spark plugs have become worn or have been installed incorrectly, they may not be able to ignite the air/fuel mixture in the engine’s cylinders, resulting in a misfire.
2. Malfunctioning ignition coils: Ignition coils are responsible for supplying high voltage to the spark plugs, wich is necessary for igniting the air/fuel mixture in the cylinders. If one or more of these coils has become faulty, it can result in a misfire due to inadequate or no spark being produced.
3. Vacuum leaks: Vacuum leaks can occur when there is a breach in the engine’s vacuum system, and this can disrupt the air/fuel ratio within the cylinders, resulting in an inefficient combustion process and ultimately leading to a misfire.
The Sensation of an Idle Misfire
An idle misfire feels like your engine is running roughly or shaking. You may even hear a popping sound coming from the engine. When you press the accelerator, you may feel a lack of power or a hesitation before the engine starts to accelerate. The engine may surge or stall and it might produce a lot of smoke from the exhaust.
Causes of Misfire at Low RPM
A misfire at low RPM is typically caused by a lack of spark to ignite the air/fuel mixture in the cylinder. This can be due to bad spark plugs, a faulty distributor cap, or damaged wiring. If the spark plugs are not firing correctly, it can prevent the gas/air mixture from burning and cause a misfire. Additionally, a clogged fuel filter or a vacuum leak can also cause an engine misfire at low RPM. Finally, an incorrect ignition timing setting can also cause misfires.
Can a Cylinder Misfire be Fixed?
Unfortunately, a cylinder misfire cannot fix itself. A misfire is usually a sign of a larger problem such as an issue with the spark plugs, fuel system, or other parts of the engine. A single misfire might dissipate and your engine may return to normal speed after a few seconds, but other misfires will likely occur in the future if the root cause is not addressed. It’s best to have your engine checked by a professional mechanic to identify and address any underlying issues.

Causes of Misfire in Sensors
There are two main sensors that can cause a misfire in a fuel-injected engine: an oxygen sensor and a mass airflow sensor. The oxygen sensor is responsible for monitoring the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases, allowing the engine’s computer to adjust the air/fuel ratio accordingly. The mass airflow sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine so that it can adjust the fuel delivery to maintain optimal performance. If eithr of these sensors are failing, they may give incorrect data to your engine’s computer, resulting in a misfire. Additionally, if any of the vacuum lines that connect to these sensors become disconnected or broken, they can also cause a misfire.
The Most Severe Type of Misfire
The most severe type of misfire is a Type A misfire. This type of misfire indicates imminent damage to the catalytic converter and is usually accompanied by a flashing Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL). When this occurs, a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is set and freeze frame data is stored. If you experience a Type A misfire, it’s important to seek immediate service from a qualified mechanic.
Signs of a Failing Coil Pack
A failing coil pack can manifest with a number of symptoms, including a rough idle, an unexplainably louder-than-usual engine, a noticeable lack of power, a significant drop in RPMs while accelerating for no apparent reason, a blinking or intermittently activating check engine light, and an active gas warning light when the vehicle has plenty of gasoline. In addition to these symptoms, you may also experience misfires and increased exhaust emissions. If any of these symptoms become apparent it is important to have the coil pack checked by a professional mechanic as soon as possible.
Can Changing Spark Plugs Fix a Misfire?
Yes, in many cases changing your spark plugs can help to fix a misfire. Spark plugs are responsible for creating the spark that ignites the fuel mixture in the engine, so if they are damaged or old, they may not be able to create a strong enough spark. Replacing your spark plugs is a relatvely simple and inexpensive process that could potentially fix your misfire. However, it is important to keep in mind that there may be other causes of a misfire, and replacing your spark plugs may not necessarily fix the problem. If you are still having issues after replacing the spark plugs, it is recommended to take your car to a qualified mechanic for further diagnosis and repairs.

Diagnosing a Rough and Shaking Idle in a Car
If your car is idling rough and shaking, it could be due to a variety of issues. The most common causes are faulty spark plugs, a failing ignition coil, clogged or dirty fuel injectors, a vacuum leak, low fuel pressure, an EGR valve that is stuck open, a faulty mass airflow sensor, or worn out motor mounts. To diagnose the issue further, you may want to check the spark plugs and coils for wear and tear. You should also check for any vacuum leaks in the intake manifold or hoses. Ensure that your fuel pressure is within the manufacturer’s recommended range by uing a fuel pressure gauge. If necessary, you can clean or replace the fuel injectors. Lastly, if your motor mounts are worn out or broken, they should be replaced as soon as possible in order to dampen engine vibration and prevent further damage.
The Effects of Low Oil on Engine Misfire
Yes, low engine oil can cause a misfire. This occurs when the oil pressure drops too low, which affects the timing of the valves and causes them to open and close at the wrong times. This disrupts the normal combustion process and causes a misfire. Additionally, a damaged oil filter can reduce the flow of oil, resulting in improper valve timing and a misfire. It is important to ensure that your vehicle’s oil levels are regularly checked to prevent potential issues such as a misfire.
Cost of Fixing an Engine Misfire
The cost of fixing an engine misfire depends on the cause of the misfire. Generally, repairs and replacements range between $100 and $1,000. Depending on the complexity of the misfire, you may need to replace certain parts such as spark plugs, spark plug wires, a distributor cap or rotor, fuel injectors, or even an entire fuel system. Additionally, you may need to inspect and possibly replace the catalytic converter or exhaust system. All these parts can add up in cost if they need replacement. Therefore, it is important to diagnose the root cause of the misfire before attempting any repairs.
Causes of Intermittent Misfires
Intermittent ignition misfires can be caused by several diferent components in the ignition system. Faulty spark plugs, spark plug wires, ignition coils, and ignition coil drivers located in the ECM are all potential sources of intermittent misfire. In order to properly diagnose and repair the issue, it is important to perform a thorough inspection of all components in the vehicle’s ignition system. It is recommended to begin with a visual inspection of all parts for any signs of wear or damage. Once any potential issues are identified, further testing should be done to confirm the diagnosis. This may involve checking for faulty connections, replacing worn out components, or performing an engine compression test.
Causes of Sputtering at Low RPMs in Cars
Your car sputtering at low RPM cold be caused by a few different things. It could be an issue with your engine’s air filter—if it’s clogged or dirty, it will restrict airflow to the engine and cause sputtering. It could also be an issue with your fuel filter, injector, or pump—these components are responsible for delivering fuel to the engine, so if they’re not functioning properly, your car may not get enough fuel and sputter at low RPM. To determine the exact cause of your car’s sputtering, it’s best to take it to a mechanic who can inspect the system and repair any problems.
Fixing a Misfire Easily
The easiest way to fix a misfire is to check the spark plugs and the ignition coils. If they appear to be in good condition, then you should check the fuel system. Make sure that the fuel filter is clean, and that there are no clogged or damaged vacuum lines. If everything looks okay, then you should try replacing the spark plugs and ignition coils with new ones. If this doesn’t solve the problem, then it could be an issue with your engine’s timing, so you’ll need to consult a professional mechanic to diagnose the problem accurately.
Conclusion
In conclusion, car misfires at idle can be caused by a variety of issues, including bad spark plugs, faulty distributor cap, bad wiring, incorrect air/fuel mixture, single injector needing cleaning, and vacuum leaks. To prevent misfires, it is important to regularly check the condition of your spark plugs and wires and replace them if necessary. If you experience a misfire at low RPMs, it is important to take your car to a qualified auto technician who can diagnose and repair the issue as soon as possible.
