Do you know that enzymes can be reused? Yes, it is true! Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts for biochemical reactions and can be used over and over again. They are not changed by the reaction, so they can be used an almost unlimited amount of times.
Enzymes are incredibly important for biochemical processes in living organisms. They speed up chemical reactions, allowing them to occur at lower energy levels. Once a reaction is complete, the enzyme remains unchanged and can bind another substrate molecule, enabling it to be reused many times.
Each enzyme has an active site or a catalytic site – this is where the substrate binds and undergoes a reaction to form products. It’s important to note that enzymes need to operate at certain temperatures and pH levels in order to work effectively. If the conditions do not meet their preferences, then the enzyme may stop working or become denatured altogether.
So why should you care about enzymes being reusable? Well, knowing this can help us understand how biochemical reactions work better and how we might be able to use enzymes in different applications such as food production or medicine. For example, we cold use enzymes to break down toxins or complex molecules into simpler ones with fewer steps required in the process.
Overall, enzymes are incredibly useful proteins that can be reused multiple times for biochemical reactions without being changed or destroyed. This makes them an invaluable tool for scientists who are researching biochemistry or looking for ways to make life easier through enzyme-aided processes such as food production and medicine applications.
Reusing Enzymes: How Many Times is Possible?
Enzymes can be reused an almost unlimited number of times as long as they remain active and stable. Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts for biochemical reactions, meaning they speed up the rate of a reaction without being changed in the process. Therefore, enzymes can be used multiple times without losing their effectiveness or changing their structure.
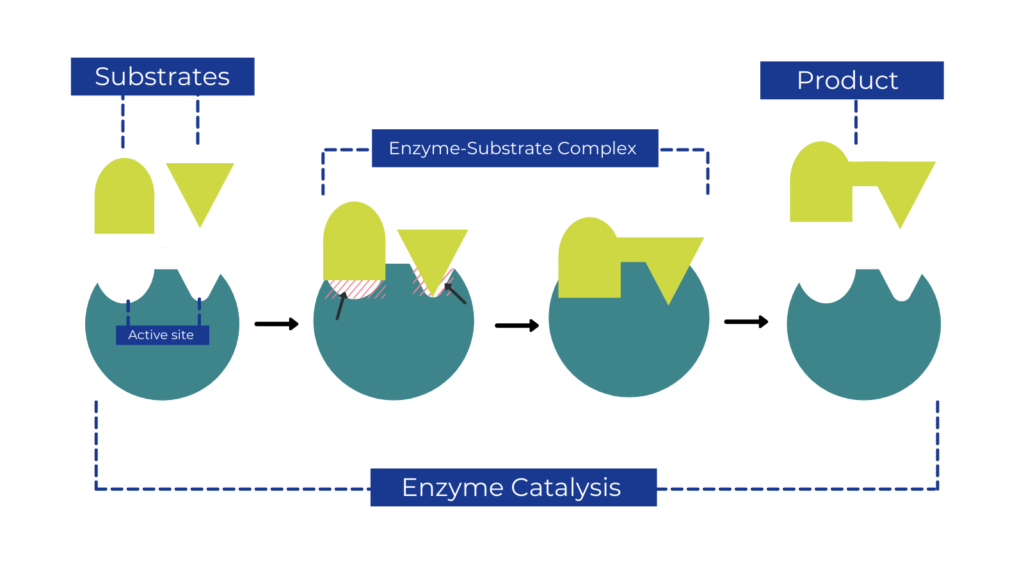
Reusability of Enzymes in the Same Reaction
Yes, enzymes can be reused for many runs of the same reaction. Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts, meaning they lower the energy required for a reaction to occur. This means that once an enzyme has been used to catalyze a reaction, it is not used up or destroyed in the process and can be subsequently reused. Furthermore, enzymes work most efficiently within a specific temperature range and pH level. As long as these conditions are maintained, enzymes can be reused multiple times to catalyze the same reaction.
Reusability of Enzymes with a New Substrate
Yes, enzymes can be reused with a new substrate. After the reaction has taken place, the enzyme remains unchanged and can bind to another substrate molecule. This is due to the fact that the active site or catalytic site of an enzyme is specific and designed to interact with certain molecules known as substrates. The enzyme’s active site is not affected by the reaction, so it can be used again and again with different substrates. This allows enzymes to be reused in multiple reactions, making them an invaluable tool in many biological processes.
Do Enzymes Have a Limited Lifespan?
No, enzymes do not last forever. Enzymes are proteins that are produced by living organisms to help with biochemical reactions. Over time, these enzymes become less active due to a process called enzyme inactivation. This occurs when the enzymes lose their shape, which prevents them from functioning properly. Factors such as heat, pH levels, and chemical denaturation can all contribute to the inactivation of enzymes. As a result, enzymes will eventually become inactive and not last forever.
Do Enzymes Undergo Permanent Changes?
No, enzymes do not permanently change. They act as catalysts, providing an alternative reaction pathway that increases the rate of reaction without being consumed or changed in the process. Enzymes remain unchanged at the end of a reaction and can be reused multiple times.
Reusability of Enzymes
Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts, meaning they facilitate and accelerate chemical reactions in living organisms. An enzyme’s ability to be reused makes it a highly efficient catalyst because it can be used over and over again to catalyze the same reaction, which is why we say that an enzyme is reusable. This is due to the fact that enzymes are not chemically changed or permanently altered during a reaction. Instead, the products of the reaction are released from the active sites of the enzyme, allowing oter substrate molecules to bind with the sites for another round of catalysis. Additionally, enzymes remain active throughout multiple rounds of catalysis due to their ability to maintain their three-dimensional shape even after binding with substrate molecules. Therefore, enzymes can be reused repeatedly without losing their activity or efficiency.
Do Enzymes Need to be Replaced After Each Use?
No, enzymes are not remade after every use. Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts in biochemical reactions, meaning that they speed up the rate of a reaction without undergoing any permanent change themselves. This means that enzymes can be reused multiple times, and do not need to be replaced or remade after each use. In fact, most enzymes remain unchanged throughout the entire reaction process, allowing them to be used again and again for the same reaction.
Can Enzymes Be Reused?
Yes, enzymes can be reused again and again. Enzymes act as catalysts in chemical reactions, which means they speed up the reaction without being a part of the product. This allows them to be re-used in other reactions without being consumed in the process. In fact, enzymes are extremely efficient and can be used millions of times faster than without them. This is why enzymes are so important for biochemical processes in the body, as their presence significantly accelerates reactions that would otherwise take much longer to occur.
Conclusion
In conclusion, enzymes can be reused many times because they are not changed or used up by the reaction. They remain unchanged and can bind another substrate to catalyze the reaction again. The enzyme works best in specific conditions of temperature and pH, and the active site is where the substrate binds. This allows enzymes to be used an almost unlimited number of times, making them a powerful tool in biological processes.
