Antioxidant supplements have become increasingly popular over the years as a way to fight off the effects of aging and disease. Antioxidants are compounds that prevent, reduce or delay cell damage caused by oxidative stress, which is when too many free radicals are released into the body. Free radicals are molecules with an unbalanced charge, which can cause damage to cells, proteins and DNA.
Antioxidants can be taken in supplement form or consumed throuh certain foods. Many people take antioxidant supplements as part of their daily health regimen, but it’s important to understand when the best time is to take them for optimal effectiveness.
The most common antioxidants found in dietary supplements include vitamin C, vitamin E and beta-carotene. Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin that helps protect cells from oxidative damage and helps build collagen in the body. Vitamin E is fat-soluble and helps protect cell membranes from free radical damage. Beta-carotene is an antioxidant found in fruits and vegetables that your body converts into vitamin A which helps support eye health.
When it comes to taking antioxidant supplements it’s important to consider when you should take them for maximum benefit. For most people, taking antioxidants with meals is ideal as they help protect your cells while you eat. For vitamin C and beta-carotene, it’s best to take them with food as these are water soluble vitamins that will be absorbed more quickly if taken with food. For fat-soluble vitamins like Vitamin E, it’s best to take them after meals as they will be absorbed more slowly if taken with food.
It’s also important not to exceed the recommended dosage of any antioxidant supplement as taking too much could potentially interfere with how your body adapts to exercise and even reduce some of the health benefits of exercise. Too much antioxidant supplementation could also increase your risk for certain types of cancer so it’s important to consult your doctor before starting any new supplement regimen or increasing your existing dosage levels.
In conclusion, taking antioxidants can help support overall health but it’s important to understand when the best time is to take them and not exceed recommended dosages levels in order to keep your body functioning at its optimal level!
When Is the Best Time to Take Antioxidants?
Ideally, antioxidants should be taken before meals, as the body absorbs more nutrients when they are consumed with food. Taking antioxidants with meals can help ensure that your body gets the most benefit from them. It is best to take antioxidant supplements in the morning, as this is when your body has the highest metabolic rate and therefoe can absorb more of the beneficial compounds. Additionally, taking antioxidants before meals can help protect against oxidative damage that occurs during digestion. Finally, taking antioxidants before bedtime may also help improve sleep quality by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress throughout the night.
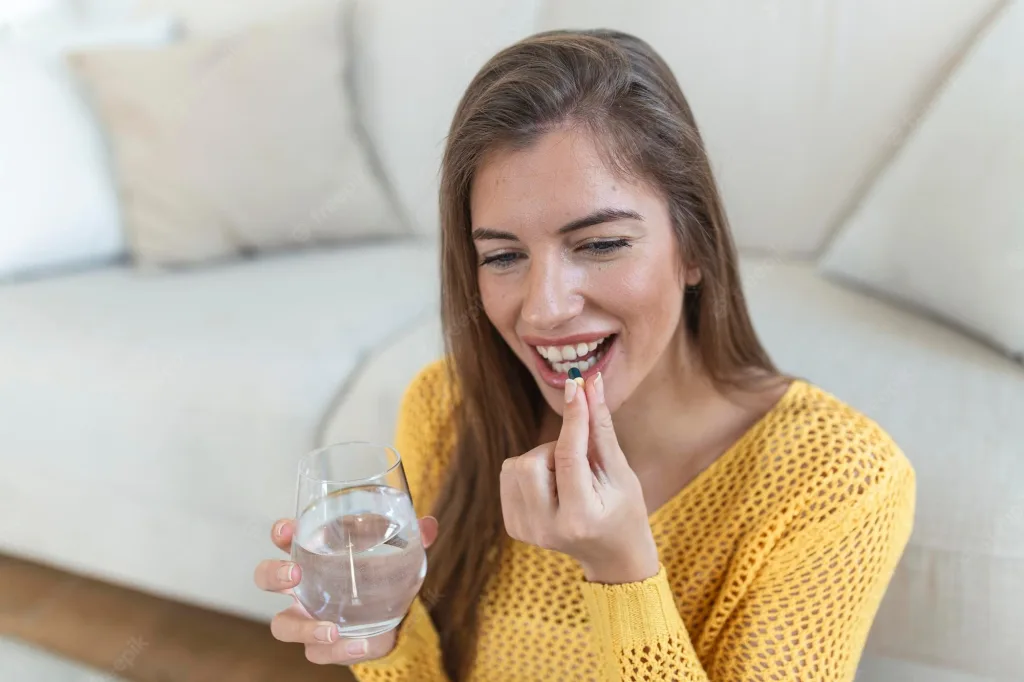

The Benefits of Taking Antioxidants Before Bedtime
Taking antioxidants at night is a great way to promote restful sleep and good oveall health. Antioxidants help the body fight off free radicals, which can cause inflammation and can disrupt the body’s natural healing processes. At night, antioxidants can help reduce stress levels, promoting better quality sleep. Additionally, taking antioxidants at night can help reduce oxidative stress that accumulates throughout the day from environmental toxins and pollutants. This helps to keep the body in balance and prevent chronic diseases from developing. Finally, antioxidants also help to boost immunity, allowing the body to better fight off infections or viruses that might otherwise disrupt sleep.
The Benefits of Taking Antioxidants Daily
Taking antioxidants every day can be beneficial for your health and wellness, but it is important to check with your healthcare provider befoe beginning any supplement regimen. Antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, can help protect against cell damage from free radicals and reduce inflammation, both of which are beneficial for overall health. However, it is important to note that some studies have found that taking antioxidants in high doses may interfere with how the body adapts to exercise and could reduce some of the health benefits associated with physical activity. Therefore, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider about an appropriate dosing regimen for you and to monitor your progress if you decide to take antioxidant supplements every day.
The Benefits and Risks of Taking Antioxidant Supplements
Taking antioxidant supplements is not a good idea. Studies have not shown any benefit to taking antioxidant supplements, and in some cases they may even be harmful. Eating a healthy diet filled with fruits and vegetables is the best way to get antioxidants. Fruits and vegetables contain other essential vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients that are beneficial to overall health whih are not found in supplements. Additionally, there is no guarantee that the amount of antioxidants in a supplement will be absorbed by the body properly or that it will reach the desired cells to provide any benefit. It is still unclear what doses of antioxidants are beneficial and safe for humans, so it is wise to proceed with caution when considering taking an antioxidant supplement.
Benefits of Using Antioxidants at Night
Yes, you should use antioxidants at night. Antioxidants can help to repair the skin while it is rejuvenating overnight. This is because the rejuvenation process gives off some by-products, like toxic free radicals, which can be captured by the antioxidants. They can also help to reduce inflammation and protect your skin from environmental damage caused by free radicals. Applying an antioxidant-rich serum or cream before you go to bed can provide your skin with extra protection and nourishment while you sleep, resulting in a brighter and more youthful complexion.

Taking Antioxidants at Night
Taking antioxidants at night may be beneficial for some people, as it can help to support brain detox efforts. However, since digestion slows down during sleep, it is generally not recommended to take supplements close to bedtime as your body may not absorb the full dose of nutrients. If you choose to take antioxidants at night, make sure to do so at least one hour before bedtime. Additionally, be sure to consult your doctor or healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
The Effects of Antioxidants on Liver Health
Yes, antioxidants can help clean your liver. Antioxidants are substances found in certain foods, supplements and herbs that can help to neutralize free radicals in the body and protect cells from damage. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cells, including cells in the liver, and contribute to conditions such as inflammation and cancer. Consuming antioxidant-rich foods or taking antioxidant supplements can help reduce the number of free radicals in the body and cleanse the liver of toxins. Examples of antioxidants include vitamin C, vitamin E, selenium and beta carotene. Additionally, there are a variety of herbal extracts that have antioxidant properties such as green tea extract, curcumin from turmeric and milk thistle extract. Including a variety of tese foods or supplements into your daily routine can help support your liver health by helping to reduce inflammation and detoxify your system.
The Benefits of Antioxidants
Antioxidants are essential for overall health and well-being. They help to protect our bodies from the damaging effects of free radicals, which are molecules that can damage our cells and contribute to the development of chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s. Here are three key benefits of antioxidants:
1. Strengthened Immune System: Antioxidants can help strengthen your immune system by neutralizing free radicals which weaken immunity. This can help to reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
2. Improved Cognitive Function: Antioxidants may help to improve cognitive function by protecting against oxidative damage to brain cells, which can impair learning, memory, and oter basic brain functions.
3. Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: Studies have shown that antioxidants may help to reduce the risk of developing certain chronic diseases such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, stroke, and some forms of cancer due to their ability to protect cells from oxidative stress damage.
Supplements That Should Not Be Taken Together
It’s important to be aware of which supplements you should not take together, as they can interfere with each other or have adverse effects on your health. Supplements such as calcium, zinc and magnesium should not be taken together, as they can reduce the absorption of each other when taken at the same time. Additionally, these three minerals are better absorbed when taken with food, so if taking them as a supplement is recommended by your doctor, it is best to take them at different meals or snacks. Iron and calcium supplements should also not be taken together, as taking them both at the same time can reduce the absorption of iron. Lastly, vitamin A and D supplements should not be taken togethr either, as taking them together can increase your risk of toxicity from vitamin A. It’s always important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen.
Source: healthline.com
The Healthiest Antioxidant
The healthiest antioxidant is a highly debated topic, but one that has been studied extensively. Many experts agree that blueberries contan the highest amount of antioxidants among all commonly consumed fruits and vegetables. Studies have shown that blueberries are a rich source of polyphenols, which are natural compounds found in plants and provide a variety of health benefits, including acting as antioxidants. Antioxidants are important for the body because they help to protect against oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals, which can lead to chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer and diabetes. In addition, blueberries are high in vitamin C, which also acts as an antioxidant within the body. Therefore, blueberries appear to be the best antioxidant among all fruits and vegetables typically eaten.
The Effects of Antioxidants on Detoxification
The short answer is no, antioxidants do not directly detox your body. However, consuming a diet rich in antioxidants can help your body reduce damage caused by free radicals, and may lower your risk of diseases that can impact detoxification. Antioxidants are molecules that interact with and neutralize free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can case cellular damage if left unchecked. Free radicals are produced as a result of normal metabolic processes like breathing or digestion, as well as from external sources such as smoking or exposure to air pollution.
Antioxidants work to neutralize and repair any potential damage caused by free radicals, which helps protect the body from illnesses such as cancer and heart disease. Additionally, antioxidants support the body’s natural detoxification process by helping to remove toxins from the liver and other organs. By boosting the natural detoxification process, antioxidants can help improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic illnesses related to toxin accumulation in the body.
In conclusion, while consuming a diet rich in antioxidants does not directly detoxify your body, it does provide many health benefits that can indirectly support detoxification.
The Effect of Antioxidants on Inflammation
Yes, antioxidants can reduce inflammation. Antioxidants are compounds that help protect our cells from damage caused by free radicals, whih can be generated by environmental factors such as UV light, cigarette smoke and air pollution. These free radicals damage our cells and lead to an inflammatory response. Antioxidants work by neutralizing the free radicals before they can cause any damage. This reduces the amount of inflammation that occurs in the body. Additionally, antioxidants can also reduce inflammation indirectly by preventing other processes that lead to inflammation such as oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation. Therefore, antioxidants are important for reducing inflammation and maintaining a healthy balance in our bodies.
The Benefits of Taking Antioxidants
The purpose of taking antioxidants is to help protect your body from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are molecules that are produced when your body breaks down food or when you’re exposed to certain environmental factors, such as tobacco smoke and radiation. By taking antioxidants, you can reduce the amount of damage that these free radicals can cause to your cells, tissues and organs. Antioxidants can help to reduce the risk of a variety of diseases, including heart disease, cancer and othr chronic illnesses. Additionally, they may help to reduce inflammation in the body and improve overall health.

Source: houstonmethodist.org
The Ineffectiveness of Antioxidant Supplements
Antioxidant supplements are not a one-size-fits-all solution and can actually be counterproductive in certain circumstances. While antioxidants are beneficial for neutralizing the damage caused by free radicals, they can also interfere with the natural immune response and impair the ability of the body to fight off bad microbes. Too high a dose of antioxidant supplementation can be toxic, as it can reduce the efficacy of other essential processes in the body, such as energy generation. Therefore, it is important to consult a physician before adding any antioxidant supplement to your diet.
Conclusion
In conclusion, antioxidant supplements can be beneficial for people who have limited access to dietary sources of antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables. However, it is important to remember that taking high doses of antioxidant supplements can interfere with the body’s natural adaptation to exercise and may even reduce the health benefits of exercise. Therefore, it is best to consult a doctor before taking any antioxidant supplement, especially vitamins C and E. Eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables should be sufficient for maintaining healthy levels of antioxidants in the body.
