Are you looking for a way to soar through the skies with minimal effort? Gliding is an incredible activity that allows you to have an adrenaline-filled adventure without having to expend too much energy. To make sure your gliding experience is as smooth and enjoyable as possible, it’s important to understand the concept of aspect ratio in gliders.
Aspect ratio is the ratio between the length and width of an aircraft’s wing. The higher the aspect ratio, the better performance you can expect from your glider. Generally speaking, most glider wings have very high aspect ratios – their span is very long compared to their width – because this helps reduce drag while producing lift (known as induced drag). The greater the aspect ratio of a wing, the lower its induced drag will be.
Wingtip devices, or winglets, are also used to improve performance by reducing turbulence near the tip of a wing. This can help increase efficiency and reduce drag even further. In terms of traditional wingspan measurements, many gliders feature an aspect ratio of 6:1; meaning that for every six feet of length, there will be one foot in chord (width).
Achieving optimal performance with your glider depends on properly understanding aspect ratio and choosing a model that best suits your needs. With careful consideration gven towards selecting a model with an appropriate aspect ratio for your specific application, you will be able enjoy a thrilling yet efficient ride through the sky!
Understanding the Aspect Ratio of a Glider
Aspect ratio is the relationship between the wingspan and chord of a glider. It is expressed in a ratio, such as 6:1, meaning the wingspan is 6 times longer than the chord. A higher aspect ratio reduces drag, increases lift and improves gliding performance. The most efficient gliders have an aspect ratio of around 10 to 16, but depending on the type of glider, an aspect ratio of 6:1 or lower can still povide good performance. Aspect ratio also helps determine how suitable a glider is for certain types of flying, such as aerobatics or racing.
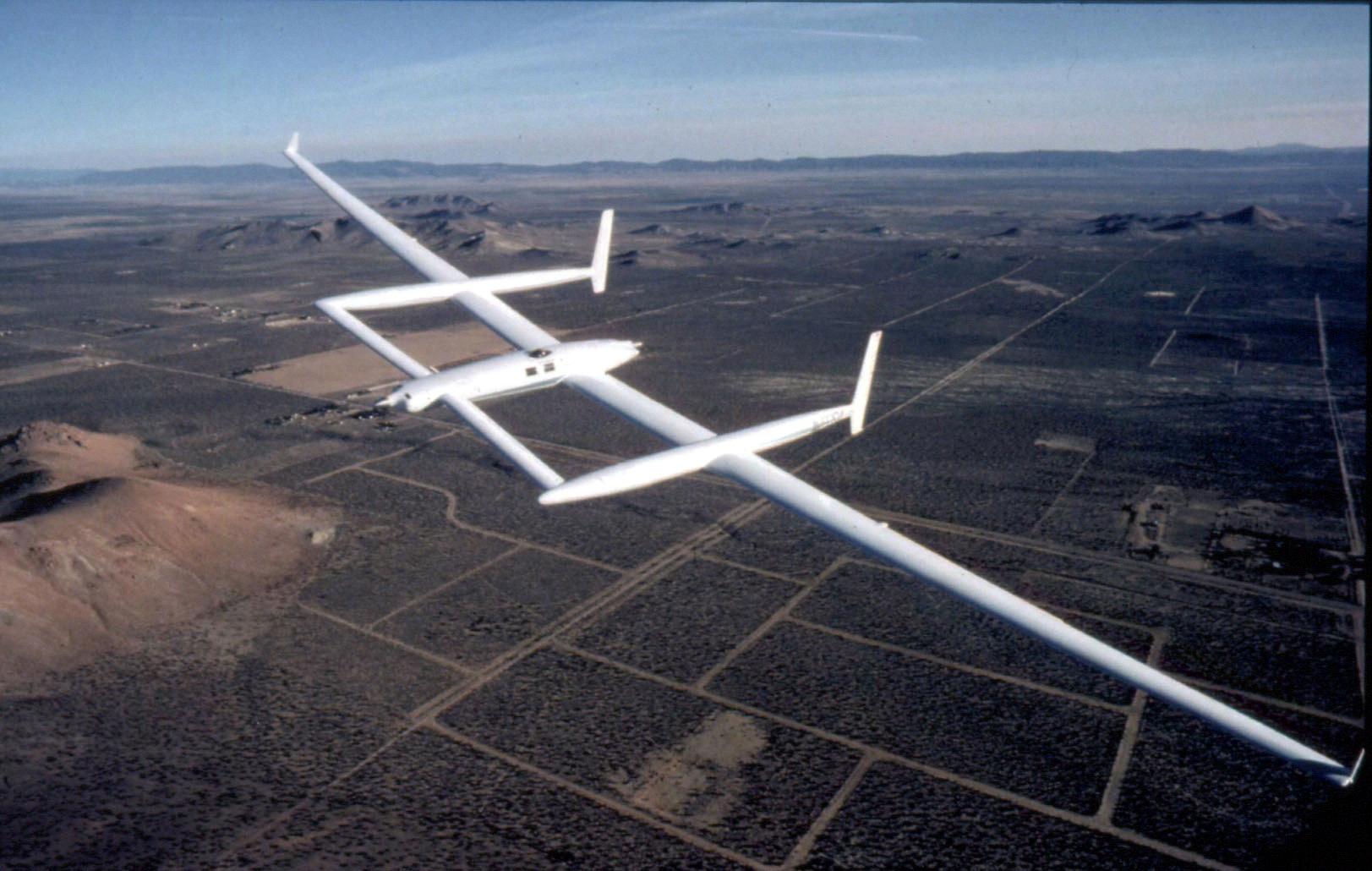
Source: hushkit.net
The Importance of Aspect Ratio in Aircraft Design
The aspect ratio of an aircraft is a measure of the length-to-width ratio of its wings or propellers, and is an important factor in determining how it will fly. A higher aspect ratio indicates a longer and narrower wing or propeller, wich typically results in an aircraft that flies more efficiently at high speed and altitude, but at the cost of greater resistance to turning. Conversely, a lower aspect ratio indicates a shorter, wider wing or propeller, which can provide better maneuverability but may have reduced speed and altitude capability. The aspect ratio of a wing also affects other factors such as lift coefficient, drag coefficient, lift to drag ratio (L/D), and stall speed. Thus, choosing the right aspect ratio is essential for achieving optimal performance from an aircraft.
The Benefits of High Aspect Ratios for Gliders
Gliders have high aspect ratios to reduce drag and improve efficiency. Aspect ratio is the length-to-width ratio of a wing, with a higher aspect ratio meaning the wing is longer and narrower. By increasing the aspect ratio of the glider, more lift can be generated with less drag since it reduces both form drag and induced drag. A higher aspect ratio also creates more efficient airfoil shapes, allowing the glider to fly faster and furher while using less energy. Wingtip devices, or winglets, are also used to reduce drag by reducing vortices created at the tips of wings. These winglets help to keep air attached to the tips of wings for longer, creating less turbulence and thus reducing induced drag.
The Aspect Ratio of a Glider
Yes, a glider has a high aspect ratio. This is because the long wingspan of a glider helps to reduce the induced drag that is created when producing lift. The induced drag can account for a significant portion of the total drag on a glider, and so having a longer wingspan allows for the drag to be reduced and thus improving the efficiency of the aircraft. In addition to this, the higher aspect ratio also provides more lift at higher angles of attack, allowing for more maneuverability and better performance in thermals.
The Importance of Aspect Ratio in Aircraft Design
Aspect ratio is an important factor in aircraft design. It affects the aerodynamic performance of the aircraft, and can have a big impact on its overall efficiency. A high aspect ratio generally indicates long, narrow wings which are better at producing lift and reducing drag, making them more efficient than short, wide wings. This alows an aircraft to fly further distances with less fuel and provides increased manoeuvrability. Low aspect ratio wings, on the other hand, are best suited for fast manoeuvres such as take-off and landing or combat operations. Aspect ratio is also important for stability when flying at low airspeeds, as higher aspect ratio wings produce more lift at lower speeds. Additionally, higher aspect ratios provide a greater range of lift coefficients which can be used to reduce stall speeds, allowing for safer and smoother flight operations.
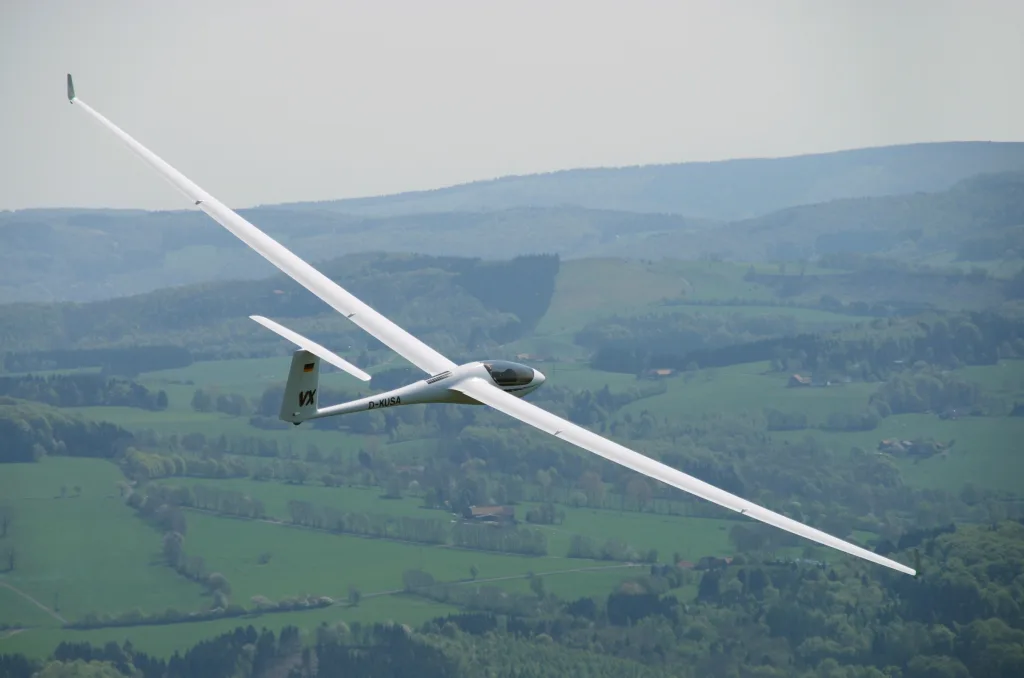

Understanding the Meaning of a 10:1 Glide Ratio
A 10 to 1 glide ratio means that for every 10 feet the airplane travels forward, it descends 1 foot in altitude. This is the distance the airplane will travel with power off. To put it another way, a 10 to 1 glide ratio means that a single unit of forward motion is exchanged for one unit of altitude lost. This ratio is often used as an indication of how efficient an aircraft is at gliding.
The Origin of the Term ‘Aspect Ratio’
Aspect ratio is a term used to describe the proportional relationship between the width and height of an image or screen. The term was originally used in the motion picture industry to describe the proportional relationship between the width and height of a frame of film, but has since been adopted for use with digital images and screens. The word “aspect” refers to how something appers when viewed from a certain angle or perspective, while “ratio” simply refers to a numerical comparison between two values. Since aspect ratio describes how the width and height of an image compare to each other, it seemed like an appropriate name for the concept.
The Importance of Aspect Ratio
Aspect ratio is an important factor in photography and video because it directly affects what each image or frame looks like. It defines the proportions of the width and height of an image, film, or video, and is expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. The fist number represents the width and the second number represents the height.
Aspect ratio is important because it determines how much of an image you will be able to see when you view it on different devices. For example, if you take a photo with a 4:3 aspect ratio and view it on a computer monitor which has a 16:10 aspect ratio, some parts of your photo will be cut off since they do not fit within the 16:10 frame. Aspect ratio also affects composition since different ratios will result in different cropping of your image.
Another reason why aspect ratio is important is because it can influence how someone perceives an image or video. An image with a wider aspect ratio (e.g., 16:9) could give viewers a sense of vastness or expansiveness that would not be conveyed by an image with a narrower aspect ratio (e.g., 4:3). This can be especially useful if you are trying to communicate certain moods or feelings in your work.
Finally, aspect ratio also affects how large or small your final output will be if you are printing out an image or viewing it on another device. A landscape photo shot with a 4:3 aspect ratio will appear larger than one shot with a 2:1 aspect ration when both images are printed out at the same size paper.
Overall, aspect ratio plays an important role in photography and videography because it dictates how much of your composition you can see on differnt devices, how people perceive your work, and how large or small your output will be when printed out or viewed on other screens.
Understanding Aspect Ratio and Its Uses
The aspect ratio is a proportional relationship between an image’s width and height, and is expressed as a formula of width to height (e.g. 3:2). It’s used to describe the shape of an image, or to determine how an image will be displayed on a screen or printed onto paper. For example, if you have an image with an aspect ratio of 4:3 and it needs to fit into a frame that has an aspect ratio of 2:1, then it wold need to be cropped in order for it to fit correctly. Aspect ratios are also important for video formats, as different formats have different aspect ratios (e.g. 16:9 or 4:3). Knowing the aspect ratio helps you make sure your video looks the best it can when viewed on any device.

Source: twitter.com
Understanding the Meaning of a 9:1 Glide Ratio
A 9:1 glide ratio means that for every 9 units of forward travel, the aircraft will lose 1 unit of altitude. For example, if the aircraft has an altitude of 1,000 feet, it can glide for about 9,000 feet (9 times 1,000). This is a typical value for small planes such as the Cessna 172, which has a maximum lift-to-drag ratio (L/Dmax) of 9. This means that the plane will be able to fly further while using less energy than other types of aircraft.
Increasing the Speed of a Glider
A glider moves faster when it is able to generate more thrust, which is the force that propels it forward. This can be accomplished in severl ways, such as increasing the angle of attack or using a higher wing loading. Increasing the angle of attack will cause the glider to cut through the air more efficiently, while increasing the wing loading will help increase lift and reduce drag. Additionally, improving aerodynamic efficiency by reducing drag and turbulence can also help increase speed.
The Impact of Aspect Ratio on Wing Performance
Aspect ratio is an important parameter that affects the performance of an aircraft wing. It is defined as the ratio of the wing’s length to its average chord, and impacts both lift and drag forces. A higher aspect ratio means a longer and thinner wing, which produces more lift with less drag. This allows for greater efficiency at low speeds and higher maneuverability at high speeds. At the same time, high aspect ratio wings are more prone to stalling at lower angles of attack compared to wings with lower aspect ratios. On the othr hand, low aspect ratio wings produce less lift but more drag which leads to increased fuel consumption and decreased maneuverability. In conclusion, aspect ratio has a significant impact on an aircraft’s performance, therefore it must be carefully considered when designing aircraft wings for optimal performance in different conditions.
The Aspect Ratio of an Aviation Wing
The aspect ratio of a wing in aviation is a measure of its aerodynamic efficiency. It is defined as the square of the wingspan (the distance from one wingtip to the other) divided by the wing area. A higher aspect ratio indicates a longer, narrower wing, whih generates less induced drag and is more efficient in flight. A lower aspect ratio indicates a shorter, wider wing, which produces more induced drag but may offer better maneuverability or stability. Generally speaking, aircraft with higher cruise speeds tend to have higher aspect ratios, while those designed for slower flight have lower ratios.

Maximizing Glider Flight Distance
A glider is able to fly the farthest when it has a set of wings with large airfoils that are slightly turned up at the tips. The larger airfoils help to create more lift, and the upturned tips help to reduce drag and create more lift. Additionally, a long slender fuselage will also help to reduce drag and increase the distance a glider can fly. Furthermore, using lighter materials such as balsa wood or carbon fiber in the construction of the glider can also help to increase its range, as it reduces its overll weight without sacrificing strength or stability. Ultimately, by combining all of these design elements, a well-designed glider can fly farther than one that is not designed with these features in mind.
Increasing the Aspect Ratio of a Glider
The aspect ratio of a glider can be increased by increasing the span of the wings while keeping the wing area constant. This will decrease the wing chord, which in turn reduces induced drag at the same lift coefficient. As a consequence, the optimum gliding speed will also be lowered, resulting in lower parasitic drag. To increase the span of your glider, you can either increase the length or width of your wings. Additionally, you may want to consider using stiffer and lighter materials when constructing your wings to further reduce weight and improve performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gliders are designed to reduce drag and improve efficiency. This is achieved by increasing the aspect ratio of the wing, which means making the length of the wing much greater than its average chord. Additionally, wingtip devices, commonly known as winglets, can also be used to reduce drag and improve performance. As a result of tese design features, gliders are capable of achieving improved fuel economy and reduced noise levels.
