Welcome to my blog about cations and their charges!
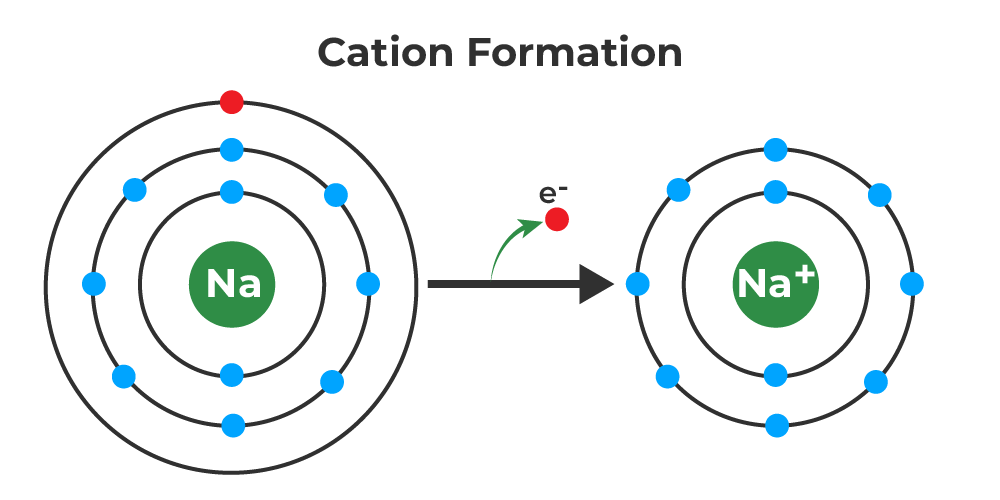
A cation is an ion with a positive charge. It is formed when an atom or molecule loses one or more electrons, giving it more protons than electrons. Cations are found in all types of compounds, including salts, acids, and bases.
The alkali metals in group 1 are always +1 when they form cations. The alkaline earth metals in group 2 are always +2 when they form cations. Other elements can also form cations with a variety of charges depending on the number of electrons lost or gained.
Cations can be identified by their behavior in solution. Positively charged ions will migrate toward the negative electrode (anode) in an electrical field, while negatively charged ions will migrate toward the positive electrode (cathode). This behavior can be used to separate different types of ions from each other.
In addition to the charge of a cation, its size is also important to consider. Larger ions such as sodium and magnesium have larger radii than smaller ions such as lithium and potassium, which allows them to fit into larger structures and form stronger bonds with other atoms or molecules. This is why some cations can act as catalysts for certain chemical reactions while others cannot.
Cations are essential components of life as we know it. For example, sodium and potassium ions play important roles in nerve impulses, muscle contraction, and pH balance within cells. Calcium ions are important for blood clotting and bone formation. Iron is essential for transporting oxygen around the body via hemoglobin molecules in red blood cells.
In summary, cations are positively charged ions that are formed when atoms or molecules lose one or more electrons. They have a variety of charges ranging from +1 up to +4 depending on the number of electrons lost or gained by the atom or molecule forming the ionic bond with another atom or molecule. Cations play important roles in many biological processes as well as beig essential components of salts and acids used in chemistry experiments and everyday life!
Positive or Negative Charge of a Cation
Cations are positively charged ions. They are created when an atom or molecule gains one or more electrons, causing it to have a net positive charge. Anions, on the other hand, are negatively charged ions created when an atom or molecule loses one or more electrons, resulting in a net negative charge.
Are Negative Ions Cations?
No, a negative ion is not a cation. Cations are positively charged ions, meaning they have lost one or more electrons and therefore have more protons than electrons. On the oter hand, negative ions, or anions, are negatively charged because they have gained one or more electrons and therefore have more electrons than protons.
Is +1 a Cation?
Yes, +1 is a cation. A cation is an ion with a positive charge, so any ion with a numerical charge of +1 is a cation. Cations are formed when atoms or molecules lose electrons, which can happen in chemical reactions or throuh electrolysis. Alkali metals in group 1 on the periodic table usually form cations of +1 charge, while alkaline earth metals in group 2 usually form cations of +2 charge.
The Relationship Between Cations and Anions
Cations are atoms or molecules that have been stripped of one or more electrons, resulting in a net positive charge. This happens beause the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom is greater than the number of electrons. Anions, on the other hand, are atoms or molecules that have gained one or more electrons, resulting in a net negative charge. This happens because the number of electrons is greater than the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom. To summarize, cations have a positive charge because they have lost electrons, while anions have a negative charge because they have gained electrons.
The Negative Charge of Anions
Anions are negative due to teir excess of electrons. In an atom, the number of protons must be equal to the number of electrons in order for the atom to be neutral (have no net charge). When there is an unequal number of protons and electrons, the atom takes on a net charge. Anions have more electrons than protons, resulting in a net negative charge.
Is the Cathode Positive or Negative?
A cathode is a negatively charged electrode. This means that it carries a negative charge and has an excess of electrons. It is the opposite of an anode, which is positively charged and has a deficiency of electrons.
The Effects of Negative Ions
Negative ions, also known as anions, are atoms or molecules that have gained an extra electron. Anions can be found in both organic and inorganic compounds and are typically very reactive due to their extra electron. Examples of common anions include chloride (Cl-), sulfate (SO4-2), nitrate (NO3-), and hydroxide (OH-). Negative ions can form when compounds dissolve in water, when air molecules break apart due to radiation, or during chemical reactions. In general, negative ions are beneficial to health and have been linked with improved air quality, lower stress levels, and better overall health.
Gaining or Losing of Electrons by Cations
Cations, or positively charged ions, form when atoms (usually metals) lose electrons. Since an ion can only have a positive charge if it has more positively charged protons than negatively charged electrons, cations must lose electrons in order to bcome positively charged.
Difference Between Anion and Cation
Answer 2: The major difference between anion and cation is the charge they carry. Anions are atoms or molecules that have a negative electric charge, usually due to the presence of extra electrons. Cations, on the other hand, are atoms or molecules with a positive electric charge, which is typically caused by the loss of electrons from ther outer electron shell. Both anions and cations can be found in nature as well as created artificially in laboratories. Anions and cations also differ in molecular size and strength of attraction to other particles. Anions tend to be larger than cations, and their attraction for other particles is greater due to their negative electric charge.
Is Cu2+ a Cation?
Yes, Cu2+ is a cation. This means that it has a positive charge due to the fact that it has lost two electrons. Cations are typically formed when an atom loses one or more electrons, leaving the atom with a net positive charge. In the case of Cu2+, it has lost two electrons, resulting in its positive charge.
Is Sodium (Na+) a Cation or Anion?
Sodium (Na+) is a cation, which is a positively-charged ion. It’s found in many compounds, including table salt (sodium chloride), and it’s also the most abundant cation in seawater. Cations are formed when an atom loses one or more of its electrons, resulting in a positive charge.
Remembering That a Cation is Positive
A helpful way to remember that a cation is positively charged is by using the mnemonic “Cats have paws ? Cations are pawsitive.” This phrase helps to associate the idea of a cat, whch has paws (or claws) that are positive, with the idea that cations are also positively charged. It’s an easy way to remember the difference between cations and anions, as cations are always positive and anions are always negative.
The Positive Charge of Anodes
The anode is positively charged because it is connected to the positive terminal of the battery. This cuses an excess of positive charge to build up on the anode, attracting negative ions (anions) from the electrolyte solution. The negatively charged anions are then attracted to the anode, where they give off electrons and become oxidized. The electrons given off by the anions flow through the electrical circuit, providing current and energy to power whatever device is connected to it.
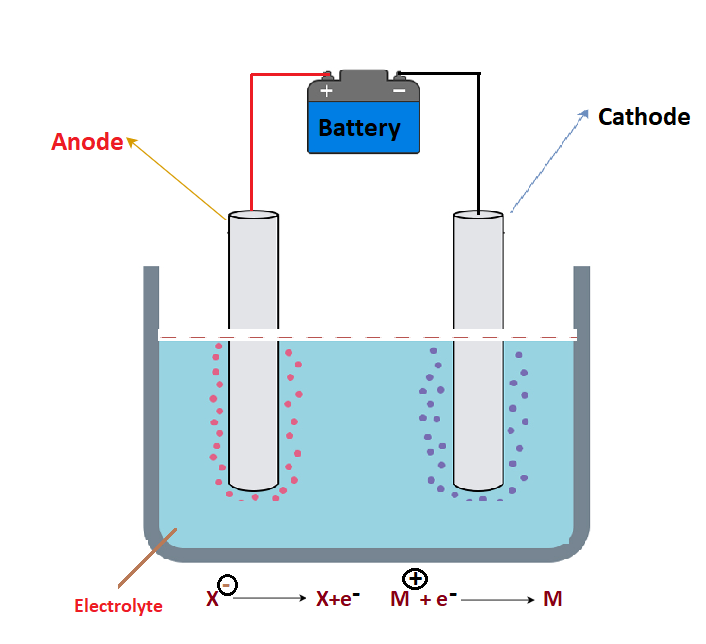
The Significance of Cathode Being Negative and Cation Being Positive
The cathode is negatively charged because electrons are removed from it in the process of electrolysis, while cations are positively charged because they gain electrons at the cathode. The overall reaction taking place at the cathode is a reduction reaction, meaning the negative electrons from the cathode are accepted by the cations, causing them to become more positive in charge. This imbalance of charges is what causes the electrolytic process to take place.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cations are positively charged ions that are formed when atoms or molecules lose one or more electrons. The alkali metals in group 1 are always +1 when they form cations, while the alkaline earth metals in group 2 are always +2 when they form cations. Cations play an important role in many different areas of science, from chemistry to biology and beyond. They have a variety of applications and can be used to create compounds, catalyze reactions, and even povide electrical power. Understanding cations is essential for anyone studying or researching the sciences.
