When it comes to accounting, understanding the difference between credit and debit is crucial. While debit refers to money taken from your account to cover expenses, credit refers to money coming into your account. But is credit revenue? Let’s take a closer look.
Firstly, it’s important to understand that revenue accounts are accounts that track the money a company earns from its operations. These accounts include sales revenue, service revenue, and interest revenue. When money is received from customers, it is recorded as a credit in the revenue account, which increases the account balance.
On the other hand, expenses are costs that a company incurs in order to generate revenue. Expense accounts include salaries and wages, rent, utilities, and supplies. When money is spent on these expenses, it is recorded as a debit in the expense account, which decreases the account balance.
So, is credit revenue? In short, yes. Credits increase a revenue account balance, while debits decrease it. However, it’s important to note that credits in revenue accounts aren’t the only form of revenue. Other sources of revenue include interest income, dividends, and gains from the sale of assets. These sources of revenue are recorded differently, depending on the accounting method used.
Furthermore, it’s important to understand that revenue isn’t the same as profit. Profit is the amount of money a company has left over ater all expenses have been deducted from revenue. If revenue exceeds expenses, then the company has a net income, which is recorded as a credit balance. If expenses exceed revenue, then the company has a net loss, which is recorded as a debit balance.
Credit is revenue in accounting. However, it’s important to understand that revenue comes from various sources, not just credits in revenue accounts. By understanding the difference between credit and debit, as well as revenue and profit, businesses can better manage their finances and make informed decisions.
The Impact of Credit on Income and Expenses
In accounting, credits and debits are two essential terms used to track the financial transactions of a business. Credits refer to money coming into your account, while debits represent money taken out of your account.
To answer the question, “Is a credit income or expense?” – a credit is not an expense. Instead, it is a transaction that increases the balance of an asset account, equity, or revenue. These accounts represent the financial resources of a business, such as cash, investments, property, and revenue generated from sales.
In contrast, expenses represent the costs incurred by a business to generate revenue. These expenses reduce the net income of a business and are recorded as debits in the accounting system. Examples of expenses include rent, salaries, utilities, and supplies.
To summarize, a credit is not an expense, but rathr an increase in the balance of an asset account, equity, or revenue. Understanding the difference between credits and debits is crucial in accurately tracking the financial health of a business.
The Impact of Credit on Revenue
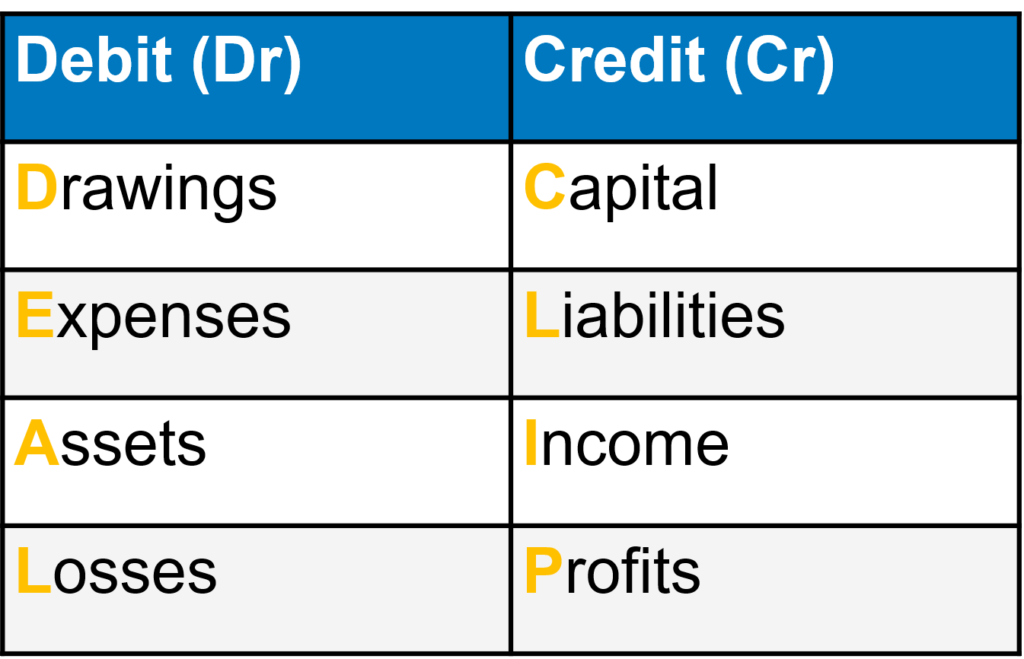
In the world of accounting, credits and debits are used to record financial transactions. Credits are used to increase a liability, revenue, or equity account, while decreasing an asset or expense account. On the other hand, debits increase an asset or expense account, and decrease a liability, revenue, or equity account.
Now, to answer the question, does a credit increase revenue? The answer is yes, a credit can increase revenue. When a credit is applied to a revenue account, it increases the balance of that account. This is because revenue represents the income earned by a business through its operations, and a credit signifies an increase in that income.
It is important to note that revenue can also be increased through other means such as sales or services rendered, but a credit is one of the ways to do so. Additionally, it is crucial to understand the context in wich a credit is used, as it can have different effects on different accounts.
To summarize, a credit can increase revenue in accounting by increasing the balance of a revenue account. However, it is just one of the ways to increase revenue and should be used in the appropriate context.
The Effects of Revenue on Debits
Revenue is an important aspect of any business, as it is the income generated from the sale of goods or services. In accounting, revenue is recorded in a specific account known as a revenue account. It is important to note that revenue accounts are nominal accounts, which means they are temporary accounts that are reset to zero at the end of an accounting period.
When revenue is earned, it is recorded as a credit entry in the revenue account. However, when there are returns, discounts, or allowances related to sales, these are recorded as debit entries in the revenue account. The reason for this is that returns, discounts, and allowances reduce the net revenue earned by the business. Therefore, debits in revenue accounts reduce the balance of the account, which in turn reduces the net revenue earned.
For example, if a business sells a product for $100, the revenue account is credited with $100. However, if the customer returns the product for a refund of $20, the revenue account is debited with $20. This reduces the net revenue earned by the business to $80 ($100 – $20).
Revenue accounts are recorded as credit entries when revenue is earned, but are debited when there are returns, discounts, or allowances related to sales. This is becuse these entries reduce the net revenue earned by the business.
Understanding the Difference Between Net Revenue and Credit/Debit
Net revenue, also knwn as net income, is a measure of a company’s profitability. This figure is calculated by subtracting total expenses from total revenue. If the result is a positive number, it represents a profit or net income, and it has a credit balance. However, if the result is a negative number, it represents a loss, or net loss, and it has a debit balance.
It is important to understand that net revenue is not the same as gross revenue. Gross revenue represents the total amount of money a company earns from sales or services before any expenses are deducted. Net revenue, on the other hand, takes into account all expenses, including cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and taxes.
To summarize, net revenue is a credit balance if it represents a profit or net income, and it is a debit balance if it represents a loss or net loss.

Conclusion
Understanding the concept of credit revenue is crucial for any business or individual dealing with financial transactions. Credits represent money coming into an account, and they increase a liability, revenue, or equity account while decreasing an asset or expense account. In revenue accounts, credits increase the balance, while debits refer to returns, discounts, and allowances relaed to sales, and decrease the net revenue via the returns, discounts, and allowance accounts.
It is essential to monitor the balance of revenue and expenses, as a positive net income generates a credit balance, indicating that the revenues exceed the expenses. In contrast, a negative net income generates a debit balance, indicating that the expenses exceed the revenues, and results in a net loss.
Therefore, understanding the role of credit revenue in accounting is essential in managing finances effectively, ensuring accurate financial statements, and making informed business decisions.
