Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table, which means it is one of the noble gases. Noble gases are known for being chemically inert, meaning that they don’t readily react with other elements or compounds. This is because their outermost electron shells are completely full, making them stable and not in need of forming bonds with other atoms.
Being a noble gas, argon is monatomic, which means it exists as single atoms rather than forming diatomic molecules. Diatomic molecules are molecules made up of two atoms of the same element, such as oxygen (O2) or chlorine (Cl2). These elements are known as homonuclear diatomic gases.
Argon, on the other hand, is a monatomic gas, meaning that it consists of single atoms of the element. This is because the outermost electron shell of argon is completely full, containing eght electrons. Therefore, there is no need for argon atoms to bond together to form molecules, as they are already stable on their own.
In fact, all noble gases are monatomic, including helium, neon, krypton, xenon, and radon. This is because they all have full outermost electron shells, making them stable and chemically unreactive.
Argon is not diatomic, but rather a monatomic gas. It exists as single atoms rather than forming diatomic molecules like some other elements, such as oxygen or nitrogen. This is due to the full outermost electron shell of argon, which makes it stable and not in need of bonding with other atoms.
Is Argon Monatomic or Diatomic?
Argon is a monatomic gas, which means that its molecules consist of only one atom of argon. Argon is a member of the noble gas group, and like the other noble gases, it is inert and does not readily form chemical bonds with other elements. Argon has an atomic number of 18, which means that its nucleus contains 18 protons and its electron configuration is 2-8-8. Argon is commonly used as an inert gas for welding and other industrial processes, as well as in lighting and other applications. Its monatomic nature makes it particulary useful in these applications, as it does not readily react with other elements or molecules.

The Reason Why Argon Is Not Diatomic
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is a member of the noble gas group wich is characterized by their low reactivity and stability due to the presence of a full outer electron shell. Argon is a monatomic gas, meaning that its atoms exist as individual units rather than bonding together to form diatomic molecules.
The reason why argon does not form diatomic molecules is due to its electronic configuration. Argon has a completely filled outer electron shell with eight electrons, making it highly stable and unreactive. The formation of a diatomic molecule would require the sharing of electrons between two argon atoms, which is energetically unfavorable due to the high stability of argon’s electron configuration. As a result, argon prefers to exist as individual atoms rather than bonding with other atoms.
In contrast, some other noble gases such as helium, neon, and krypton can form diatomic molecules under certain conditions. This is because their electronic configurations are not as stable as argon’s, and the formation of a diatomic molecule can provide a more stable electron configuration.
Argon is not diatomic because its highly stable electronic configuration makes it energetically unfavorable to form diatomic molecules.
Is Argon a Monatomic Element?
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It belongs to the group of noble gases, which are characterized by their extremely low reactivity. As a noble gas, argon is naturally found in its monatomic form, meaning that it consists of a single atom.
A monatomic molecule is a molecule that is composed of only one atom. In the case of argon, it exists as a monatomic molecule because it is an inert gas with a complete outer electron shell. This means that it has no tendency to form chemical bonds with othr atoms and remains as a single atom.
Other noble gases, including helium, neon, krypton, xenon, and radon, are also monatomic molecules. These elements also have a complete outer electron shell, which makes them highly stable and unreactive.
It is important to note that not all elements exist as monatomic molecules. Many elements, including oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon, exist as diatomic molecules, meaning that they consist of two atoms. For example, oxygen gas (O2) is composed of two oxygen atoms bonded together.
Argon is a monatomic molecule because it consists of only one atom. As a noble gas, argon is highly stable and unreactive, and it exists in its monatomic form naturally.
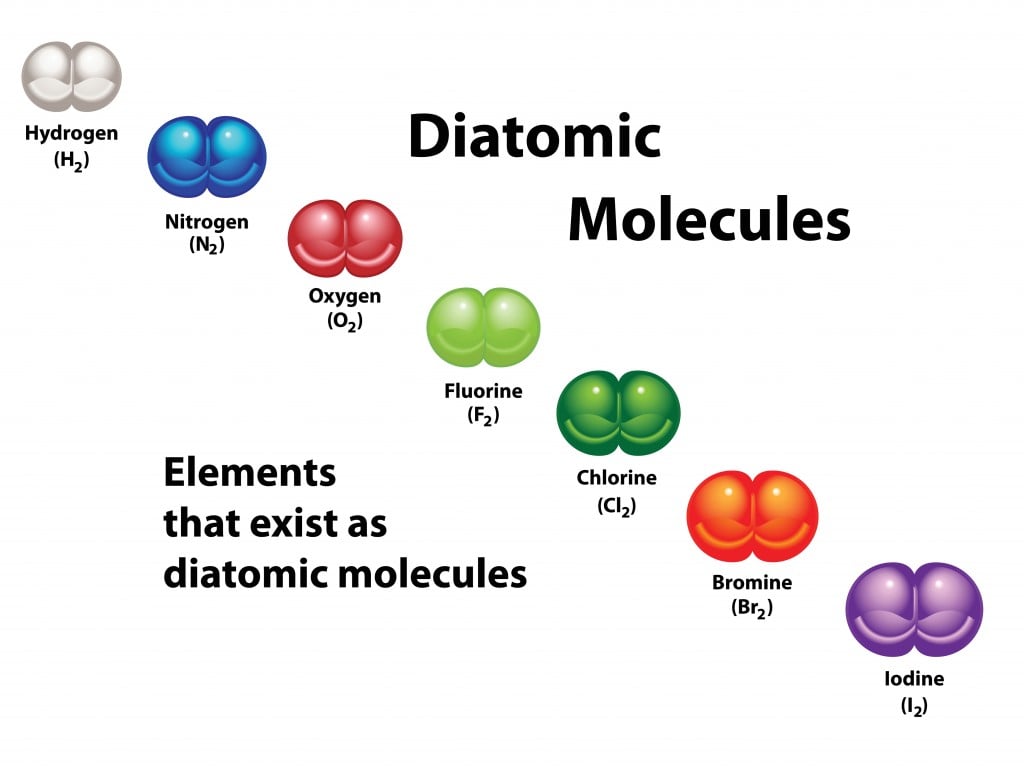
The Seven Diatomic Elements
Diatomic elements are a group of elements that exist as molecules made up of two atoms of the same element. There are seen elements that fit this description, and they are known as the diatomic elements:
1. Hydrogen (H2) – This is the most abundant element in the universe and is also the lightest element. It is used in the production of ammonia, which is used to make fertilizers, and in rocket fuel.
2. Nitrogen (N2) – This element makes up about 78% of the Earth’s atmosphere and is essential for the growth of plants. It is also used in the production of ammonia and fertilizers.
3. Oxygen (O2) – This element is necessary for respiration in living organisms and makes up about 21% of the Earth’s atmosphere. It is also used in the production of steel, plastics, and other materials.
4. Fluorine (F2) – This element is the most reactive of all the elements and is used in the production of a wide range of chemicals, including refrigerants, plastics, and pharmaceuticals.
5. Chlorine (Cl2) – This element is a strong oxidizing agent and is used in the production of a wide range of chemicals, including solvents, pesticides, and plastics.
6. Iodine (I2) – This element is used in medicine as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is also used in the production of dyes and photographic materials.
7. Bromine (Br2) – This element is used as a flame retardant in plastics and textiles. It is also used in the production of agricultural chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
The seven diatomic elements are hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, iodine, and bromine. Each of these elements has unique properties and uses in various industries.
Conclusion
Argon is not a diatomic gas. Unlike the other elements in group 18 of the periodic table, argon is a monatomic gas. This means that it exists as single atoms rather than as molecules made up of two atoms bonded together. Being an inert gas, argon is chemically unreactive and does not form diatomic molecules. Its unique properties make it usful in various applications such as welding, lighting, and as a protective gas in the production of electronics. While it may not fit into the category of diatomic gases, argon is still an important element in the world of science and industry.
