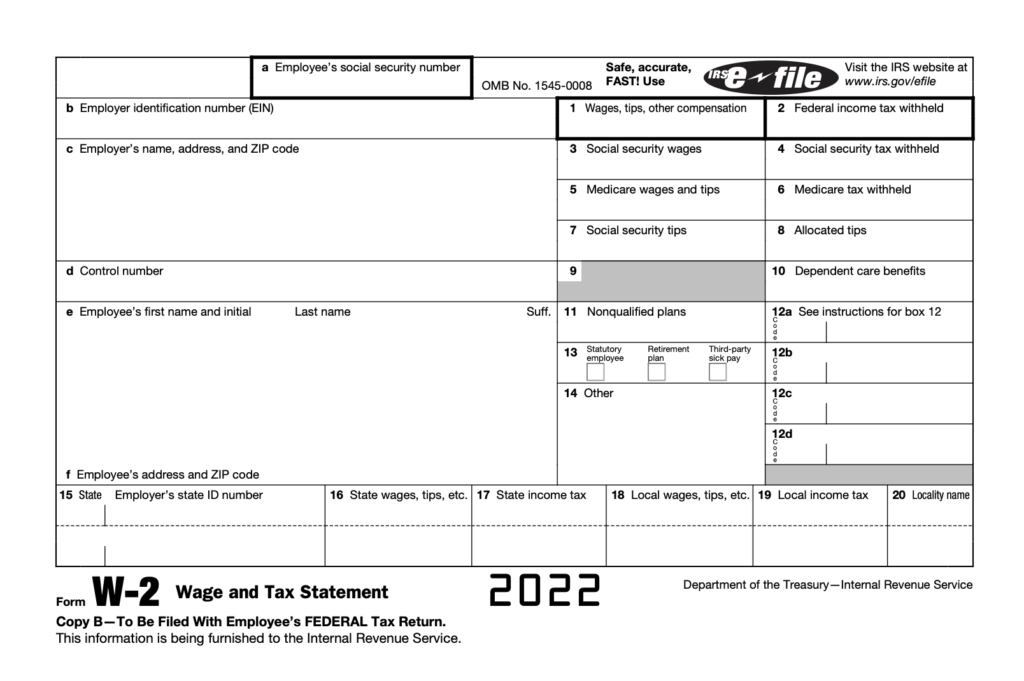
Have you ever looked at your W2 form and wondered what Box D was for? It’s a common question that many people have when it comes to their taxes. Box D is actually a control number, or an identifier that helps employers keep track of your W2 document.
This number is assigned by the company’s payroll processing software and helps employers ensure that the information they have on file is accurate and up-to-date. It can be used to verify the identity of an employee in case of discrepancies or changes to their name or address.
The control number also makes it easier for employers to match up W2 forms with other documents such as pay stubs and tax documents. In addition, it ensures that all employees receive the correct tax forms each year. Without this control number, employers wuld have difficulty ensuring accuracy across the board.
It’s important to note that you don’t need to do anything with this control number; simply enter it on your W2 form as you receive it from your employer. If you notice that your name has changed since last year, make sure to contact your employer and ask them to update their records so that everything stays up-to-date.
Overall, Box D on a W2 form serves an important purpose for both employers and employees alike by providing a way for companies to accurately track employee information and provide employees with accurate tax forms each year. So if you ever find yourself wondering what Box D is on your W2 form, now you know!
Understanding Box D/W-2
Box D/W-2 on your Form W-2 is a control number that uniquely identifies your document in your employer’s records. This number is typically assigned by the company’s payroll processing software and used to keep track of all the documents that have been issued. It is important to make sure this number matches the one on your actual Form W-2, as it can be used for tax filing purposes.

Understanding Boxes D and DD on a W-2 Form
Box D on a W-2 form is the amount of salary deferrals to a 401(k) plan. This is the amount of money that an employee has elected to have withheld from their paycheck and placed into their 401(k) account.
Box DD on a W-2 form is the total cost of employer-sponsored health coverage. This includes both employer and employee contributions, and it is reported for informational purposes only—it does not need to be reported as taxable income or deducted from any other part of the W-2 form.
Understanding the Empty Box D on My W-2
Box D on your W-2 is typically left blank because it is an optional field used by many payroll departments to assign a unique control number to a specific W-2. If your payroll department does not use this field, then it will remain blank. This does not affect your ability to report your income taxes, as the other information on your W-2 is sufficient for tax purposes.
Is Box 12 D on a W-2 Tax Form Deductible?
No, W-2 Box 12 Code D is not deductible. Your 401(k) contributions are already taken out of your wages on a pre-tax basis, which is reflected in Box 1 of your W2. This means that you do not need to deduct anything else for this on your tax return.
Is W-2 Code D Tax Deductible?
No, code D on your W-2 is not deductible. Code D represents the amount of elective deferrals you made under a Section 401(k) cash or arrangement plan, including a SIMPLE 401(k) arrangement. This amount is not taken into account when calculating your taxable income and cannot be deducted from your taxes. However, you may be eligible for the Saver’s Credit, which is claimed on Form 1040 Schedule 3, line 4.
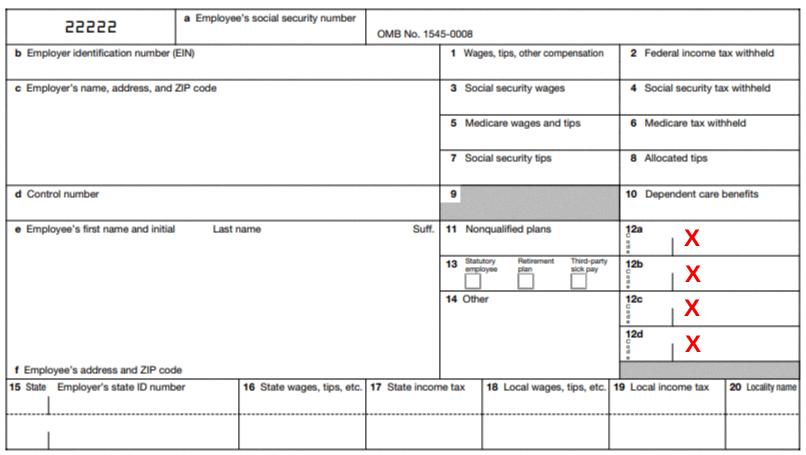
Understanding the Meaning of Box 12 on a W-2 Form
D and DD in Box 12 of the W-2 refer to the cost of employer-sponsored health coverage. The amount in Box 12 Code D is taxable, while the amount in Box 12 Code DD is not taxable. This amount includes both employer and employee contributions, and may include accident or health insurance premiums, as well as payments for long-term care insurance. Employer contributions to a Health Savings Account (HSA) are also included in this amount. The total cost of these benefits must be reported in Box 12 with Code D or DD. It’s important to note that if you are enrolled in an employer-sponsored health plan and make pre-tax contributions to the plan through your payroll deductions, those contributions shold not be included in either D or DD.
Reporting Box 12 D on Tax Returns
No, you do not have to report box 12 D on your tax return. Box 12, with code DD, is for informational purposes only and does not include any taxable amount. However, if you are enrolled in an employer-sponsored health coverage plan and the cost of that coverage is reported in box 12 with code DD, then you may want to consider it when filing your taxes. It could potentially provide some deductions or credits that could lower your tax bill.
Location of Box D on W-2 Wage and Tax Statement
Box D on a W-2 wage and tax statement can be found directly below the “employee’s name, business address, and zip code” box. This box is primarily used for reporting a control number that is provided by the Social Security Administration. The control number is usually issued when an employee first applies for a Social Security Number (SSN).
What Does the ‘DD’ Abbreviation Represent on a W-2 Form?
DD stands for “Employer-Sponsored Health Coverage Cost” and is reported on the W-2 form. It is a code used to indicate the total amount of money you, and your employer, have paid towards your employer-sponsored health coverage plan. This amount does not affect the numbers you report on your tax return—it is only provided as information.
The Consequences of an Empty Box D
If there is nothing in Box D of your W-2, it’s no problem. You can simply enter any number in the format 5 digits, space, 5 digits (e.g. 12345 67890) to satisfy the software requirements when attempting to e-file your tax return. The IRS doesn’t care what’s in Box D so you don’t need to worry about it not being filled out.
Understanding the Meaning of ‘D’ on a Tax Return
Schedule D is a form used by taxpayers to report capital gains and losses from the sale or exchange of certain capital assets. This includes stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other investments. Capital gains are profits that you gain from selling a capital asset for more than what you paid for it. Capital losses occur when you sell an asset for less than what you paid for it. Schedule D also allows taxpayers to report any involuntary conversions (such as those due to theft or casualty) of capital assets not held for business or profit.
Consequences of Not Withholding Social Security Tax for Employers
If your employer does not withhold the Social Security tax (also known as FICA tax) from your pay, you will be responsible for paying the tax yourself when you file your annual income tax return. The amount of FICA taxes due is based on your income and is 7.65% of wages earned up to $132,900 in 2020. If you exceed that amount, you may owe additional taxes. It is important to remember that even if your employer does not withhold FICA taxes, you are stil required to pay them. Failure to do so may result in penalties and interest payments when filing your return.
Is the Part D Premium Tax Deductible?
Yes, Part D premiums are tax deductible. If you are not yet collecting Social Security benefits, you can deduct these premiums from your taxes. Part D plans help cover the costs of prescription drugs, so this is a great way to save money on medications that you may need for your health. To qualify for a deduction, the premiums must be paid through payroll deductions or with after-tax dollars from your bank account. The amount of the deduction depends on your income and filing status, so it’s best to check with a tax professional for more inforation about how much of your Part D premium is deductible.
Source: patriotsoftware.com
Is Distribution Code 2 Taxable?
Yes, Distribution Code 2 is taxable. Any distribution from a retirement plan or IRA that meets the criteria of Distribution Code 2 is considered taxable income and must be reported on your tax return. Although there are some exceptions, such as distributions taken after age 59 1/2, most distributions taken with this code are taxable. Be sure to review any documentation you receive with the distribution to determine what type of taxes, if any, you may owe.
Are Dependent Care Benefits Taxable on W-2 Forms?
The answer to whether dependent care benefits on a W-2 are taxable depends on the tax treatment of the benefit. Generally, dependent care benefits are considered a non-taxable employee benefit, meaning that the amount reported in Box 10 on an employee’s W-2 form is not subject to federal income tax. However, state or local taxes may apply to these benefits in some cases. Additionally, if the dependent care benefits received by an employee exceed $5,000 for the year, then any excess amount over $5,000 may be subject to federal income tax. It is important to consult with a tax professional for specific guidance reated to your personal situation.

Conclusion
In conclusion, Box D on your W-2 is a unique control number used by many payroll departments to identify your document in their system. Although it is not mandatory to complete, it can help you keep track of your W-2 document in the event that you need to access it again. If your W-2 does not have a Control Number (box D) assigned, you can simply leave it blank and the information should still be valid.
